Carbon dioxide (CO2) Accounts for around threequarters of the warming impact of current human greenhousegas emissions The key source of CO2 is the burning of fossil fuels such as coal, oil andYou are About to View Greenhouse Gas Quantities from Suppliers Important Information about this Data Set Suppliers are facilities or entities that supply certains products (eg, fossil fuels or industrial gases) into the economy that, when combusted, released, orMajor greenhouse gases are Carbon dioxide Water Vapour Methane Ozone Nitrous oxide Chlorofluorocarbons
What Gases Are Greenhouse Gases Jean Marc Jancovici
What are the greenhouse gases names
What are the greenhouse gases names- Five Major Greenhouse Gases The most significant gases that cause global warming via the greenhouse effect are the following Carbon Dioxide Accounting for about 76 percent of global humancaused8 rows Greenhouse gas Chemical formula Global Warming Potential, 100year time horizon Atmospheric



Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Carbon Sequestration Pmf Ias
Carbon dioxide is the greenhouse gas you hear people talk about the most That's because we produce more carbon dioxide than any other greenhouse gas, and it's responsible for most of the warming Some greenhouse gases stay in the atmosphere for only a short time, but others can stay in the atmosphere and affect the climate for thousands of years List Of Greenhouse Gases 1 Carbon Dioxide (CO2) Perhaps the most wellknown global greenhouse gas is carbon dioxide It occurs naturally in 2 Methane (CH4) Methane is 25 times stronger than carbon dioxide in terms of its global warming potential It also 3 Nitrous oxide (N2O) Greenhouse gas definition Greenhouse gases are the gases which are responsible for causing the greenhouse effect Meaning, pronunciation, translations and examples
Synthetic greenhouse gases are manmade chemicals and are used in Australia for a wide variety of purposes They are most commonly used as refrigerant in air conditioning and refrigeration equipment foamblowing agents in the manufacture of polyurethane foams and in foams for thermal insulation, such as in refrigeratorsGreenhouse Gases Greenhouse gases are gases—like carbon dioxide (CO 2), methane, and nitrous oxide—that keep the Earth warmer than it would be without them The reason they warm the Earth has to do with the way energy enters and leaves our atmosphere When energy from the sun first reaches us, it does so mainly as lightLearn more about climate change and discover ways to take action
The top three companies on the newest edition of PERI's Greenhouse 100 Index are all electric power generators, and they're responsible for a full five percent of US greenhouse gas"Greenhouse gases are the gases that absorb the infrared radiations and create a greenhouse effect For eg, carbondioxide and chlorofluorocarbons" Greenhouse Gases such as carbon dioxide is the primary cause for the Greenhouse Effect The major contributors to the greenhouses gases are factories, automobiles, deforestation, etcWhen too many greenhouse gases are made, it causes more heat to get trapped in the atmosphere and the temperature increases, causing it to get warmer Look at the list of greenhouse gases below and some of the activities that humans do that cause more greenhouses gases to be made Greenhouse Gases Carbon Dioxide, CO2 Methane, CH4 Ozone, O3




Dr Robert Rohde It S A Good Question I Believe All Greenhouse Gases Other Than Co2 Ch4 N2o And O3 H2o Are Negligible Before Man I Know There Are Some



2
Two of the top countries on this list, China and India, are experiencing rapid economic growth Also on the list are the United States and European Union members—developed countries that have historically emitted and continue to emit greenhouse gases at high levels It is important to note that these ten countries produce a majority of global emissions Greenhouse Gases With The Highest Emissions Volumes Carbon Dioxide from Fossil Fuels and AgroForestry Carbon dioxide is a colorless and odorless gas composed of a carbon atom and two oxygen atoms The natural sources of carbon dioxide are volcanoes, hot springs, geysers, carbonate rocks when it is dissolved in water and acids Carbon dioxideHydrofluorocarbon transition Ecology adopted a new rule in December to transition away from using potent greenhouse gases known as hydrofluorocarbons (or HFCs) in products and equipment, starting Jan 1, HFCs are chemicals made up of hydrogen, fluorine, and carbon




Greenhouse Gas Emissions Our World In Data




Global Warming Causes Of Global Warming Britannica
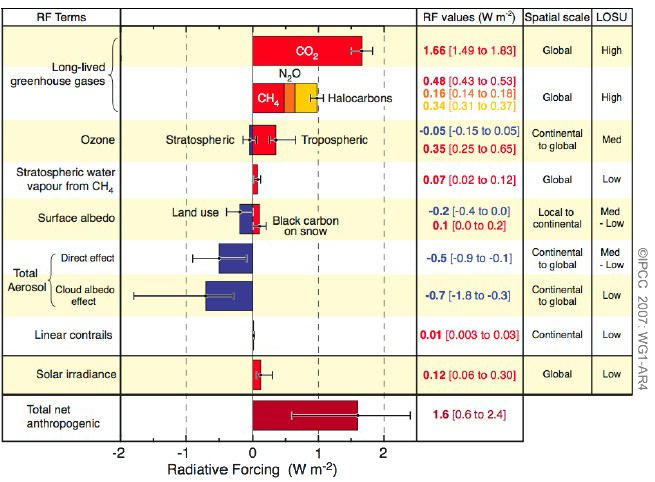
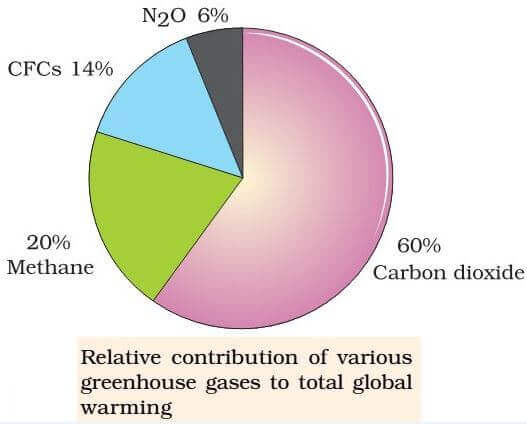
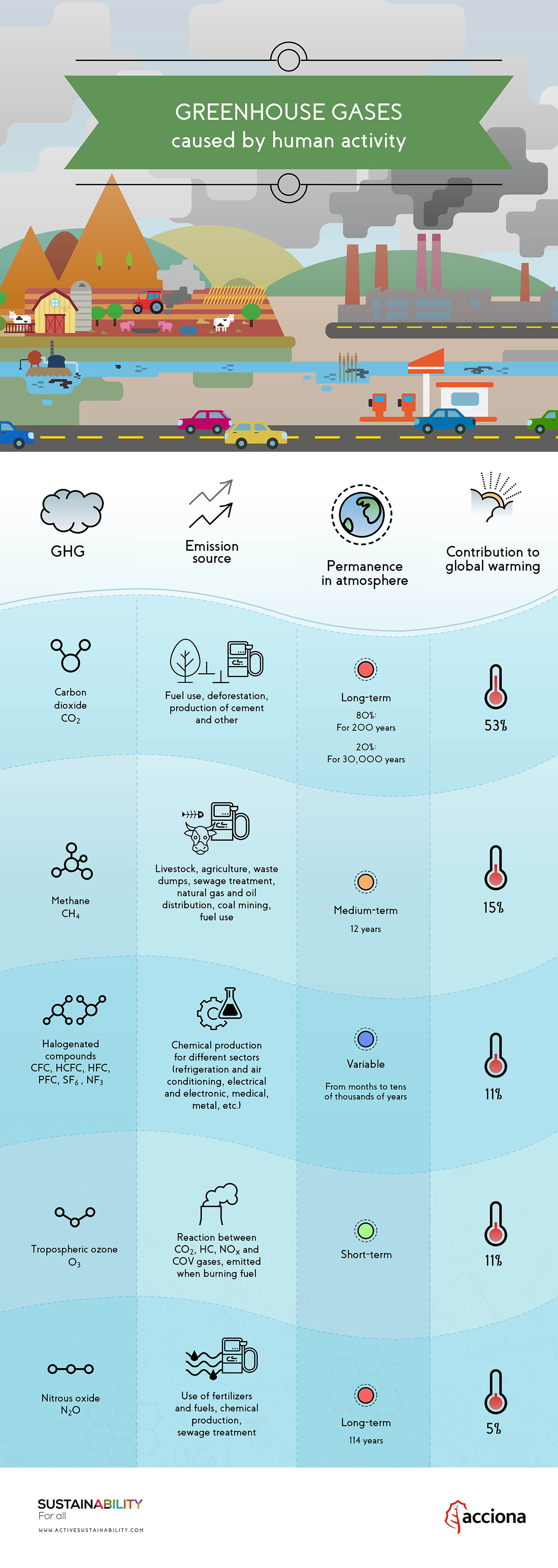
As we discussed in the previous sections, total greenhouse gas emissions are the sum of emissions of various gases carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, and smaller trace gases such as hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs) and sulfur hexafluoride (SF 6) How much does each gas contribute to global greenhouse gas emissions?Fluorinated gases Hydrofluorocarbons, perfluorocarbons, sulfur hexafluoride, and nitrogen trifluoride are synthetic, powerful greenhouse gases that Table A1 List of Greenhouse Gases and their contribution to Scotland's net greenhouse gas emissions, 18 Name of Greenhouse Gas Chemical Formula Global Warming Potential (GWP) (Conversion factor to carbon dioxide equivalent) Contribution to Scotland's Net Greenhouse Gas Emissions, 18 (in MtCO 2 e) Percentage of Scotland's Net Greenhouse Gas




Edgar Fossil Co2 Emissions Of All World Countries 18 Report European Commission Emissions Countries Of The World Purchasing Power Parity



Greenhouse Gases List Global Warming Contributors
Carbon dioxide accounts for most of the nation's emissions and most of the increase since 1990 Transportation is the largest source of greenhouse gas emissions in the United States, followed by electricity generation Emissions per person have decreased slightly in the last few yearsGreenhouse gas, any gas that has the property of absorbing infrared radiation (net heat energy) emitted from Earth's surface and reradiating it back to Earth's surface, thus contributing to the greenhouse effect Carbon dioxide, methane, and water vapour are the most important greenhouse gases (To a lesser extent, surfacelevel ozone, nitrous oxides, and fluorinated gases 5 major greenhouse gases and their sources 1 Carbon dioxide Carbon dioxide has the chemical formula CO2 It is a very harmful and damaging greenhouse gas This gas is released into our atmosphere largely through the burning of fossil fuels such as coal, oil and natural gas This is done in factories, power plants, the aviation industry, in



30 Catchy Greenhouse Gases Slogans List lines Phrases Names 21




Webquest Carbon Footprint Greenhouse Gas Carbon Footprint
At night, Earth's surface cools, releasing the heat back into the air," NASA's Climate Kids explains "But some of the heat is trapped by the greenhouse gases in the atmosphere That's what keeps our Earth a warm and cozy 59 degrees Fahrenheit, on average" This is known as the "greenhouse effect," and without it the planet wouldCarbon Dioxide Carbon dioxide, or CO2, is a greenhouse gas that is emitted by the natural carbon cycle and by human activities, such as burning fossil fuels, notes the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) Normally, CO2 gas emitted into the atmosphere is removed in roughly equal amounts by oceans and plants List of Greenhouse Gases and their contribution to Scotland's net greenhouse gas emissions, 16 Name of Greenhouse Gas Chemical Formula Global Warming Potential (GWP) (Conversion factor to carbon dioxide equivalent) 1 Contribution to




Solved Q1 A Define Global Warming Potential Gwp 3 M Chegg Com




Sustainability
Greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide (CO 2), methane (CH 4), nitrous oxide (N 2 O), ozone (O 3), and fluorinated gases Greenhouse gases allow the sun's light to shine onto Earth's surface, and then the gases, such as ozone, trap the heat that reflects back from the surface inside Earth's atmosphere Carbon dioxide (molecular weight 44) is heavier than nitrogen (28) or oxygen (32), and those are the major gaseous components of the Greenhouse gases are certain molecules in the air that have the ability to trap heat in the Earth's atmosphere Some greenhouse gases, like carbon dioxide (CO 2) and methane (CH 4 ), occur naturally and play an important role in Earth's climate If they didn't exist, the planet would be a much colder place However, some human activities, such




Greenhouse Effect Video Worksheet



How Do Greenhouse Gases Contribute To Global Warming
Greenhouse gases warm the planet Scientists know with virtual certainty that increasing greenhouse gas concentrations tend to warm the planet In computerbased models, rising concentrations of greenhouse gases produce an increase in the average surface temperature of the earth over timeThe term "greenhouse gases," or GHGs, covers a wide variety of gases that, once they are released into the atmosphere, trap the sun's heat When the sun's energy reaches the Earth's atmosphere, some of it is reflected back to space and the rest is absorbed and trapped in the lower atmosphere, heating the Earth What are the different greenhouse gases (GHG)?




15 Sources Of Greenhouse Gases




The Greenhouse Effect British Geological Survey
According to NOAA's 19 Annual Greenhouse Gas Index (right axis), the combined heating influence of all major greenhouse gases has increased by 45% relative to 1990 Graph by NOAA Climategov based on data from NOAA ESRL According to the 19 AGGI report, the combined heating influence of the longlived, humanproduced greenhouse gases is 3 Greenhouse gases are components of the atmosphere that contribute to the greenhouse effect Some greenhouse gases occur naturally in the atmosphere, while others result from human activities such By far the most abundant of the hydrofluorocarbons, trifluoromethane has an atmospheric lifetime of 260 years and traps 11,700 times as much heat as carbon dioxide 5 Ozone Usually when ozone



30 Catchy Intro Say On Greenhouse Gases Slogans List lines Phrases Names 21




Carbon Dioxide Methane Nitrous Oxide And The Greenhouse Effect Conservation In A Changing Climate
Reservoir gases make up about 13% of our total greenhouse gas emissions When land is flooded to make a reservoir, and plants and soil collect in the reservoir waters and downstream, this organic The usual way of comparing greenhouse gases is through a single conversion factor, called the global warming potential, which uses a somewhat arbitrarily chosen time horizon of 100 years For methane, this is usually given as a factor of 25 (that is, methane is 25 times more potent than carbon dioxide)That approach in effect makes carbon dioxide, CO 2, the prevailing "currency" of greenhouse gases and global warming Let's consider the principal GHGs one at a time, starting with water vapor, the most abundant greenhouse gas in the atmosphere according to NOAA's National Climatic Data Center (NCDC)



30 Catchy Greenhouse Gas Slogans List lines Phrases Names 21




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa
an email distribution list of all data providers ObsPack Name Each ObsPack data product has a unique ObsPack name using the following structure obspack_____ Please note that the part of this structure is optional Greenhouse Gases Carbon Dioxide, Water Vapor, Nitrous Oxide, Aerosols Share of Global GHG Emissions 15% A jet airliner leaves condensation trails in the sky The trails are formed by soot and water vapor from the plane engines which burn keroseneCharacteristics of the Greenhouse Effect Earth stays warm by trapping heat from the sun in the atmosphere The planet has a layer of protective gases called greenhouse gases




Greenhouse Effect 101 Nrdc




List The Gases Which Are Responsible For Greenhouse Effect
5 Notorious Greenhouse Gases Water vapor Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc Water vapor is the most potent of the greenhouse gases in Earth's atmosphere, Carbon dioxide Of the greenhouse gases, carbon dioxide (CO 2) is the most prominent Sources Sources of greenhouse gases Some greenhouse gases, such as methane, are produced through agricultural practices, in the form of livestock manure, for example Others, like CO2, largely resultThere are four primary greenhouse gases carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), nitrous oxide (N2O) and fluorinated gases These are called greenhouse gases since they contribute towards trapping heat within the atmosphere The name greenhouse comes from the greenhouse facilities used to grow our




Greenhouse Effect Video Worksheet



Meet The Greenhouse Gases Nasa Climate Kids
Before we get to greenhouse gases, we need to cover the greenhouse effect This is when heat and energy from the sun get trapped in the Earth's atmosphere Some of this is a natural process, but gases created by human activity are trapping more heat in the atmosphere, raising the temperature and causing global warming or climate change These gases are therefore known as 'greenhouse gases Greenhouse Gases Introduction Certain gases in Earth's atmosphere—particularly carbon dioxide (CO 2), methane (CH 4), and water vapor (H 2)—trap energy from solar radiation and so keep Earth warmer than it would be otherwiseThese gases are termed greenhouse gases, and the warming they create is termed the greenhouse effect or greenhouse warming About 65% of greenhouseGreenhouse gases in the atmosphere absorb heat energy and prevent it escaping into space This keeps the Earth warmer than it would be without these gases Greenhouse gases are not a
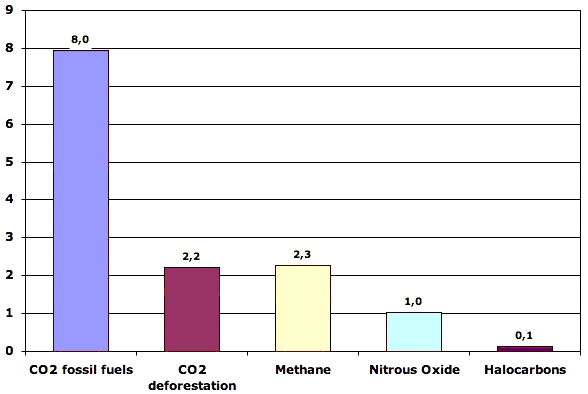



What Gases Are Greenhouse Gases Jean Marc Jancovici



1
Without them, Earth would be too cold to sustain life as we know it When we talk about greenhouse gases, we're referring to carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, hydrofluorocarbons, perfluorocarbons and sulphur hexafluoride Join us on social! Greenhouse gases Their impact on climate change Terry Gibb, Michigan State University Extension Many scientists are predicting the Earth is heading toward a global warming danger zone and humans are responsible for most of it by upsetting the balance in the natural ecosystem Climate change has been debated for a while on




Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia
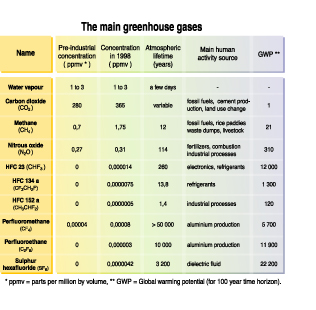



Main Greenhouse Gases Grid Arendal




Greenhouse Gases Factsheet Center For Sustainable Systems




Greenhouse Gases A Student S Guide To Global Climate Change Us Epa




Greenhouse Lab Computer Based Docsbay




Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Carbon Sequestration Pmf Ias




8 List 5 Trace Gases That Have Been Associated With Chegg Com




Pub Quiz Without The Beer Or Crisps Sorry Round 1 The Natural Causes Of Climate Change 1 Climate Refers To The Weather Experienced Over Ppt Download




Advantages Or Disadvantages Of The Greenhouse Effect By Maria Mith Medium



Emissions By Sector Our World In Data




E 3 2 List The Main Greenhouse Gases Their Sources And Discuss Their Relative Effects Youtube




B9bpss48bepfgm




Overlooked No More Eunice Foote Climate Scientist Lost To History The New York Times



30 Catchy Funny On Greenhouse Gases Slogans List lines Phrases Names 21




Ace Presentation Worksheet Version 2 Key Alliance For Climate




Appendix A List Of Workshop Participants Assessing Mechanisms For Integrating Transportation Related Greenhouse Gas Reduction Objectives Into Transportation Decision Making The National Academies Press




15 Sources Of Greenhouse Gases
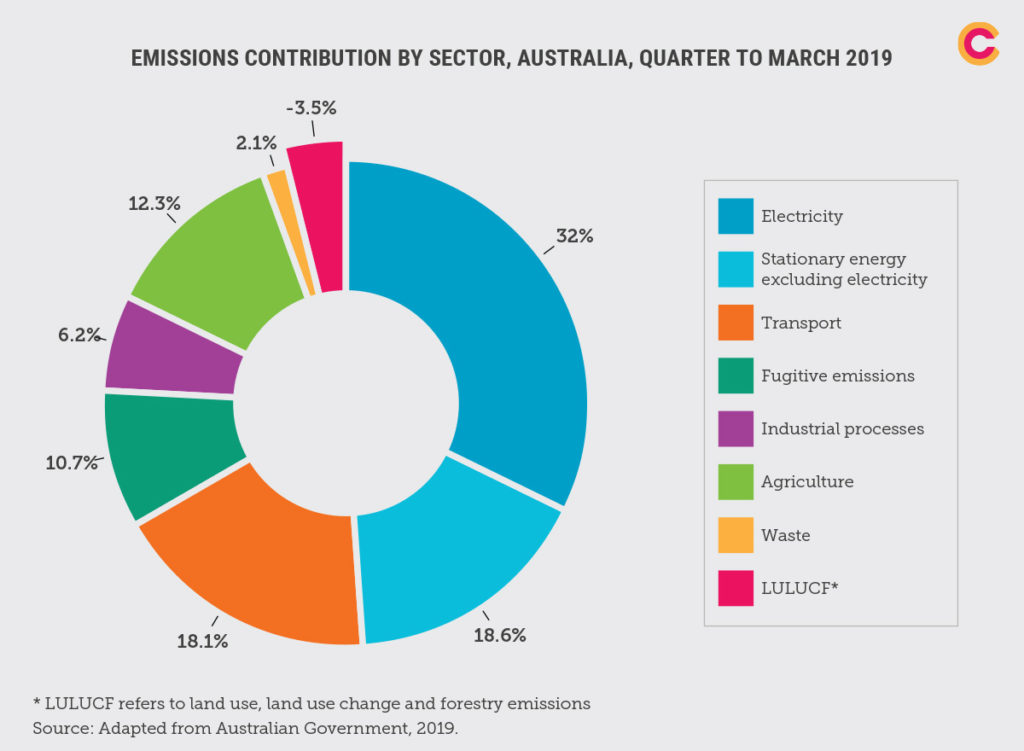



What Is Climate Change And What Can We Do About It Climate Council




Greenhouse Gas An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




E 3 2 List The Main Greenhouse Gases And Their Sources And Discuss Their Relative Effects Youtube




Carbon Intensive Industries The Industry Sectors That Emit The Most Carbon Eco Warrior Princess




Global Warming And Greenhouse Gases Civilsdaily




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa



Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia




What Gases Are Greenhouse Gases Jean Marc Jancovici




Which Gases Are Greenhouse Gases American Chemical Society



2




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa



What Are The Natural Sources Of Greenhouse Gases Quora
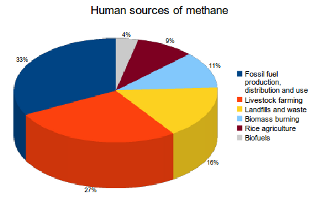



Main Sources Of Methane Emissions What S Your Impact




Greenhouse Gases A Student S Guide To Global Climate Change Us Epa



30 Catchy Reducing Greenhouse Gas Emissions Slogans List lines Phrases Names 21




Greenhouse Effect 101 Nrdc




Major Greenhouse Gas Reductions Needed By 50 Ipcc Climate Central




Name The Major Greenhouse Gases And Their Sources Brainly In
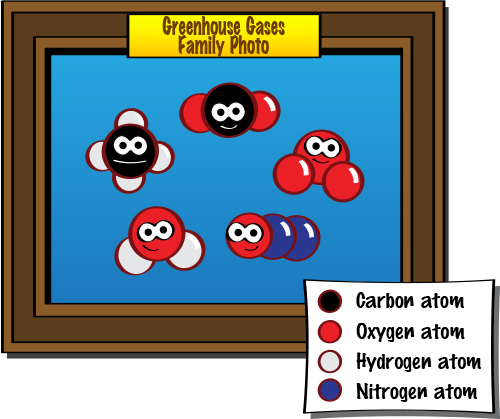



Greenhouse Effect Keeping The Balance Nasa Climate Kids



Greenhouse Gasses List Bearealfan



Q Tbn And9gctgkh3lkfqajwyepgurto9s2fnpmhyucm9nip9v1zpuftbnak Usqp Cau



30 Catchy Controlling Greenhouse Gas Slogans List lines Phrases Names 21
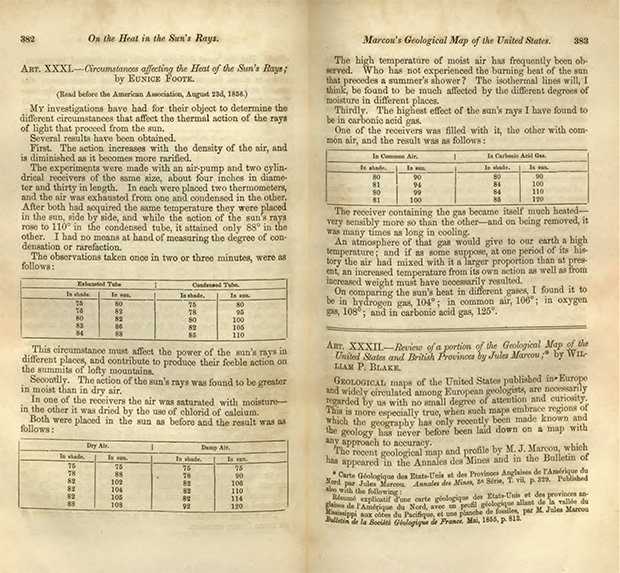



Happy 0th Birthday To Eunice Foote Hidden Climate Science Pioneer Noaa Climate Gov




What Is Greenhouse Effect List Two Green House Gasses And State The Ultimate Effect Of Green House Brainly In



2




Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia




Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia




Greenhouse Gas Emissions From Soils A Review Sciencedirect
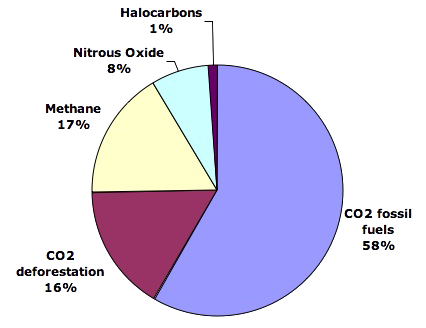



What Gases Are Greenhouse Gases Jean Marc Jancovici




Ace Presentation Worksheet Version 2




Greenhouse Gases Global Warming And The Ozone Layer Ppt Download




The Greenhouse Effect And Our Planet National Geographic Society




Low Carbon Power Wikipedia
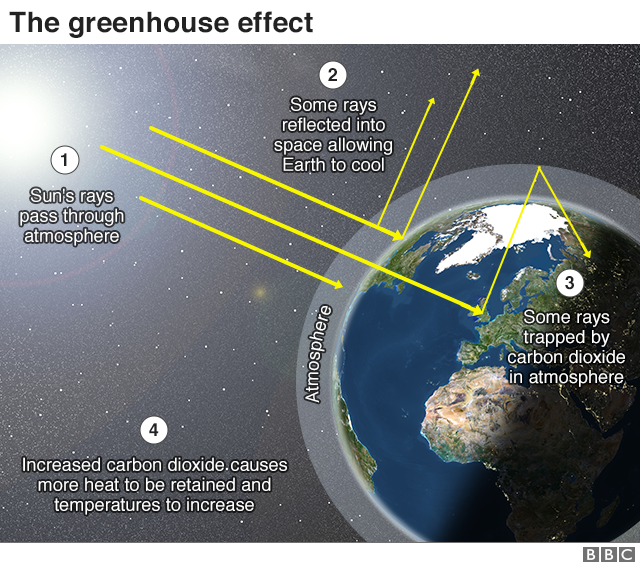



What Is Climate Change A Really Simple Guide c News




Food Production Is Responsible For One Quarter Of The World S Greenhouse Gas Emissions Our World In Data




Greenhouse Gases Presentation By Teacher Tom S Teaching Corner




Yaxis Skip Every 3 Boxes Atmosphere Line Graph



Main Sources Of Carbon Dioxide Emissions What S Your Impact



Q Tbn And9gcrevtfvebbghz5zkkbq1akjhfs4 Gwdrbwpqnmfiixo2oqlgyw8 Usqp Cau




5 Notorious Greenhouse Gases Britannica




What Is Greenhouse Effect Definition Causes And Effects
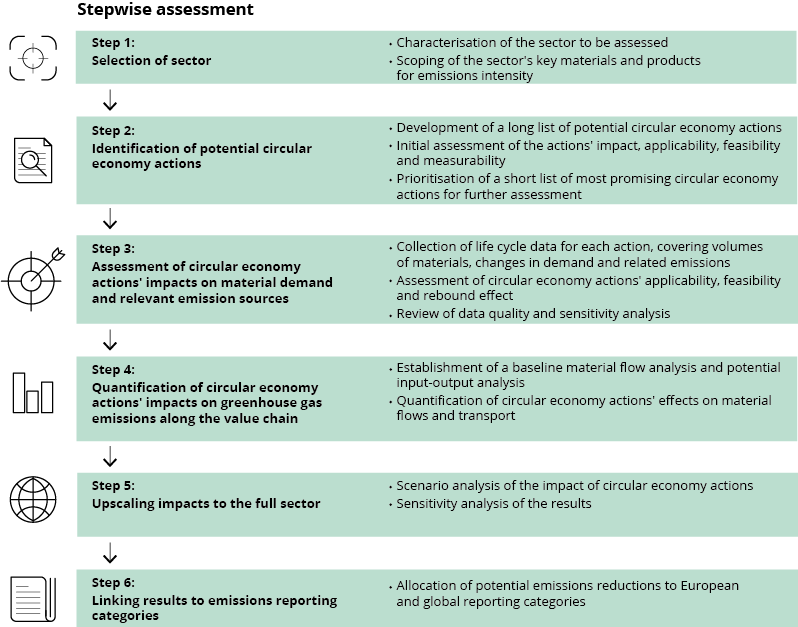



Cutting Greenhouse Gas Emissions Through Circular Economy Actions In The Buildings Sector European Environment Agency




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa




Greenhouse Effect Definition Diagram Causes Facts Britannica




List Of 59 Best Practices For Greenhouse Gas Emissions Reductions In Download Table




Types Of Greenhouse Gases Definition And Effects On Climate Change




Name Any Two Greenhouse Gases Youtube
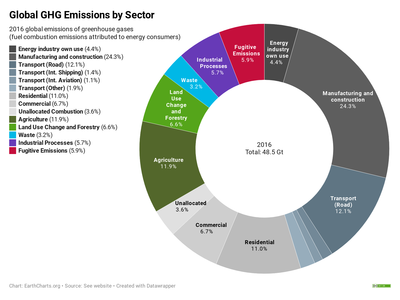



Greenhouse Gas Emissions Wikipedia




Solved Name Chem 122 Volcanoes And Acid Rain 1 Which Of Chegg Com
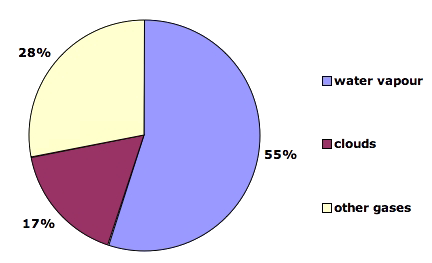



What Gases Are Greenhouse Gases Jean Marc Jancovici




The Principal Greenhouse Gases And Their Sources Neef




Which Gases Are Greenhouse Gases American Chemical Society
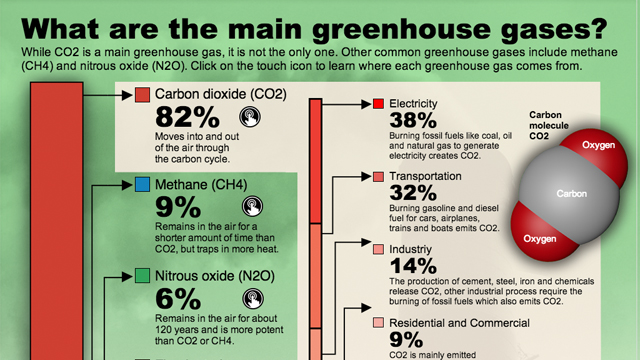



What Are Greenhouse Gases And Where Do They Come From Kqed
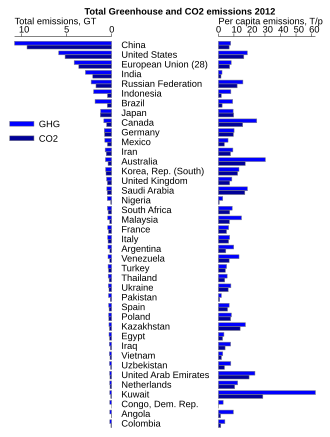



Greenhouse Gas Emissions Wikipedia
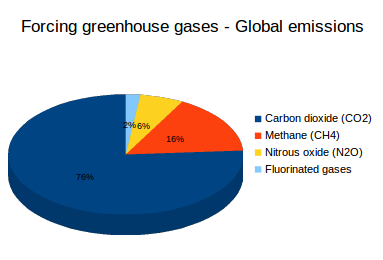



What Are Greenhouse Gases What S Your Impact




27 Greenhouse Gases Ideas Greenhouse Gases Gas Greenhouse



3




Student Worksheet Climate Change Study Guide




5 Notorious Greenhouse Gases Britannica




Solved Regarding The Greenhouse Effect By Radiative Gas Chegg Com




1 A Greenhouse Gases List Major Greenhouse Gases Chegg Com




Lists Of Green House Gases Download Table
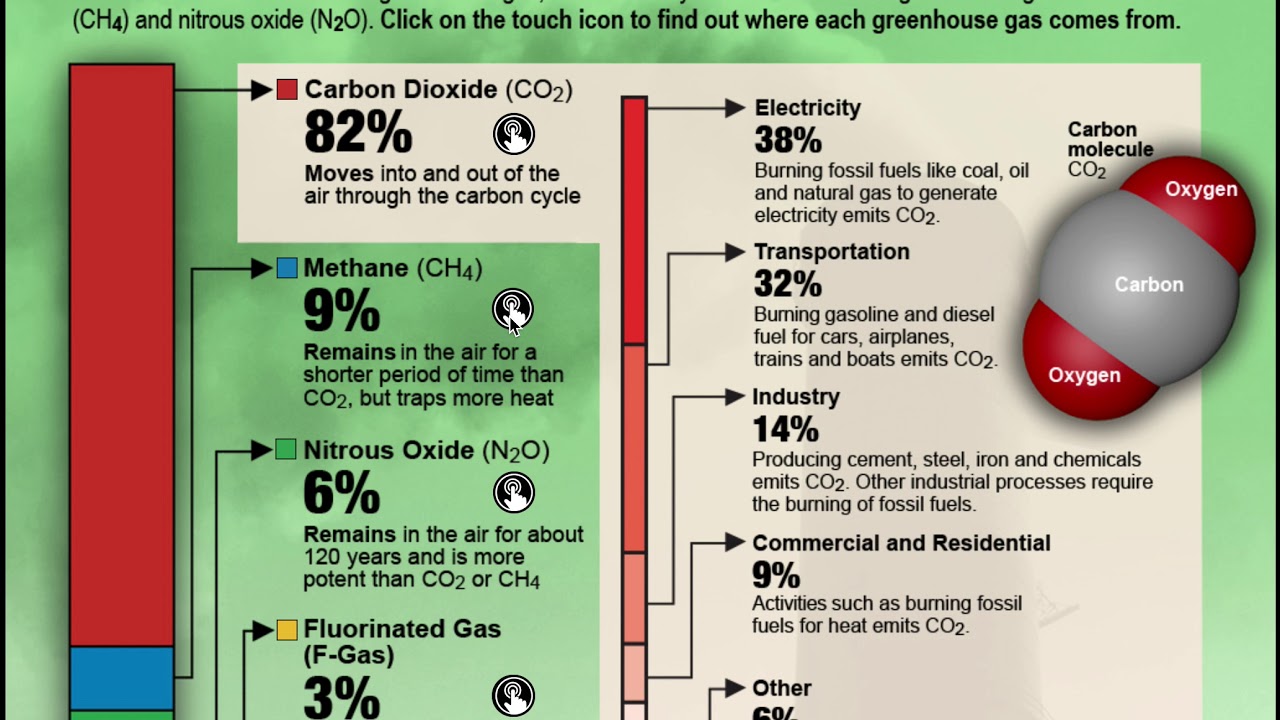



What Are Greenhouse Gases And Where Do They Come From Kqed



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿