The AGGI in was 147, which means that we've turned up the warming influence from greenhouse gases by 47% since 1990;These charts from the time show how and why the Earth's climate is changing the main greenhouse gas responsible for global warming If greenhouse gasThe Global Monitoring Laboratory conducts research on greenhouse gas and carbon cycle feedbacks, changes in clouds, aerosols, and surface radiation, and recovery of stratospheric ozone
Carbon Emissions Forestry Carbon Credits The Arbor Day Foundation
Greenhouse gases chart global
Greenhouse gases chart global-For each greenhouse gas, a Global Warming Potential (GWP) has been calculated to reflect how long it remains in the atmosphere, on average, and how strongly it absorbs energy Gases with a higher GWP absorb more energy, per pound, than gases with a lower GWP, and thus contribute more to warming Earth Daily chart Greenhousegas emissions are set and therefore greenhousegas emissions Indeed, global energyrelated carbon emissions fell by 58% in , or nearly 2 gigatonnes of carbon



Emissions By Sector Our World In Data
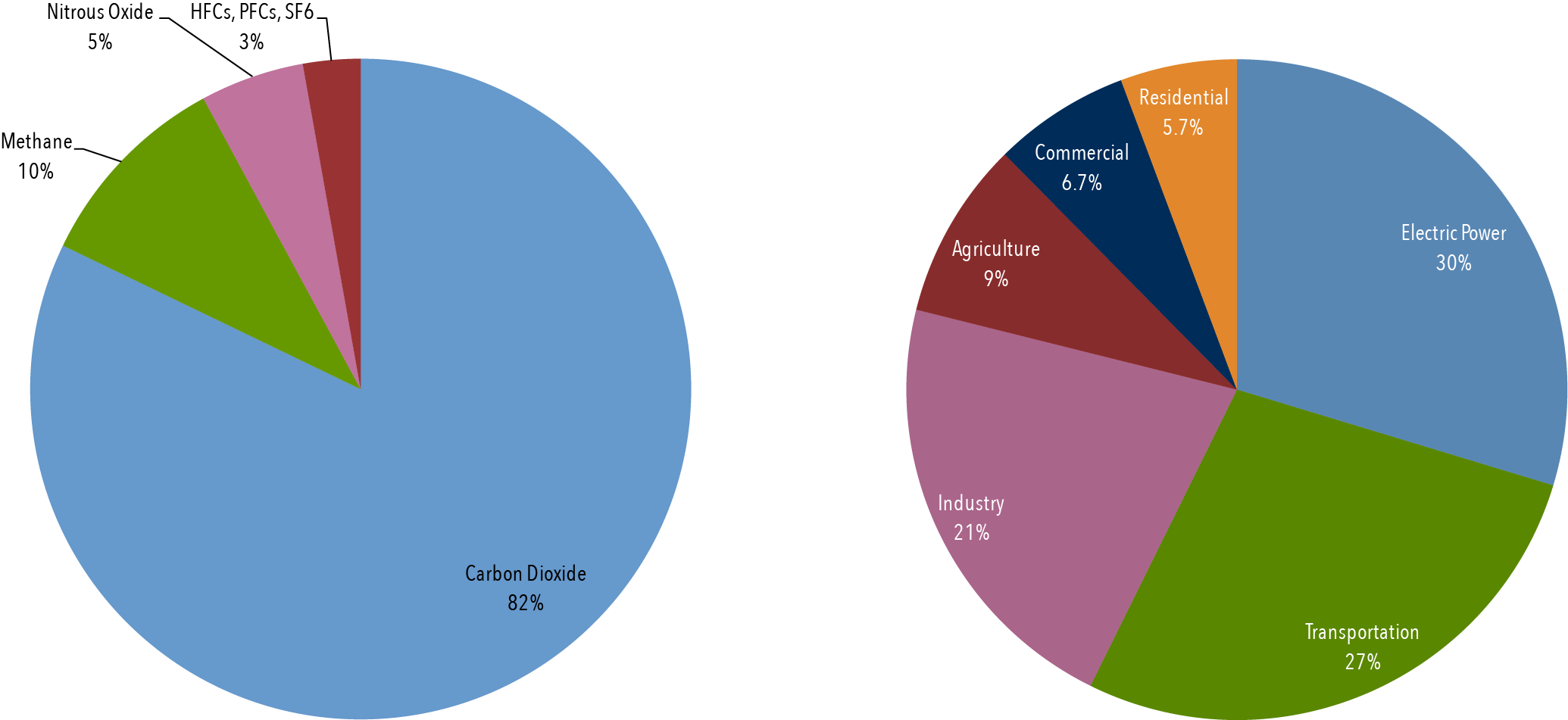
The pie chart below shows total US emissions from the US Greenhouse Gas Inventory for 18 by sector Total US emissions in 18 were 6,677 Million Metric Tons CO 2 e The pie pieces colored in blue and purple represent the sectors that contain facilities reporting direct emissions to the Greenhouse Gas Reporting ProgramIndustry (21% of 10 global greenhouse gas emissions) Greenhouse gas emissions from industry primarily involve fossil fuels burned on site at facilities 19 UK greenhouse gas emissions final figures xlsx and ods data tables updated New annex added final emissions by end user and fuel type 2 February 21
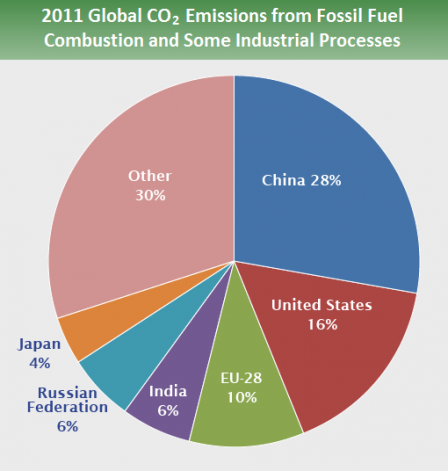
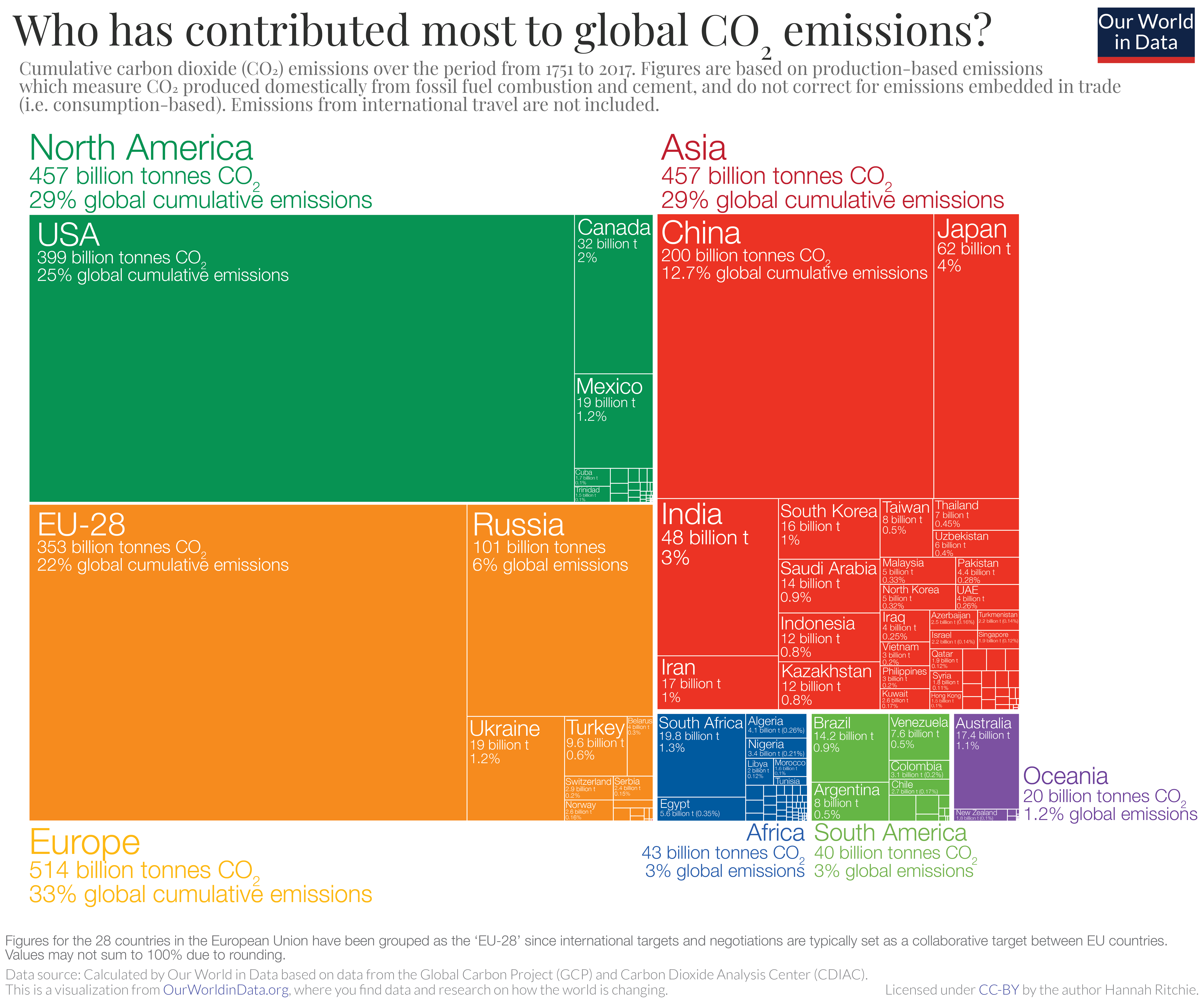
Greenhouse gas emissions are greenhouse gases vented to the Earth's atmosphere because of humans the greenhouse effect of their 50 billion tons a year causes climate changeMost is carbon dioxide from burning fossil fuels coal, oil and natural gasThe largest polluters include coal in China and large oil and gas companies, many stateowned by OPEC and RussiaAt the global level, the gases shown in the pie chart (at right) represent the key greenhouse gases emitted by human activities These gases are most closely documented in studies of anthropogenic greenhouse gas emissions Image (at right) Carbon greenhouse gas emissions by gas Source IPCC (07);This is a list of sovereign states and territories by carbon dioxide emissions due to certain forms of human activity, based on the EDGAR database created by European Commission and Netherlands Environmental Assessment Agency released in 18 The following table lists the 1990, 05 and 17 annual CO 2 emissions estimates (in Megatonnes of CO 2 per year) along with a list of
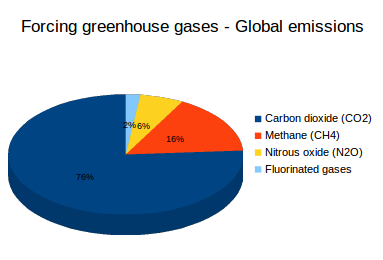
Greenhouse gases refer to the sum of seven gases that have direct effects on climate change carbon dioxide (CO 2), methane (CH 4), nitrous oxide (N 2 O), chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs), perfluorocarbons (PFCs), sulphur hexafluoride (SF6) and nitrogen trifluoride (NF3) The data are expressed in CO 2 equivalents and refer to gross direct emissionsHuman emissions of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases – are a primary driver of climate change – and present one of the world's most pressing challenges 1 This link between global temperatures and greenhouse gas concentrations – especially CO 2 – has been true throughout Earth's history 2 To set the scene, let's look at how the planet has warmed The graphic paints a picture of how that looks for each country China's emissions for energy alone make up nearly percent of total global discharge of greenhouse gases In




Carbon Emissions Forestry Carbon Credits The Arbor Day Foundation




Greenhouse Gases Copernicus
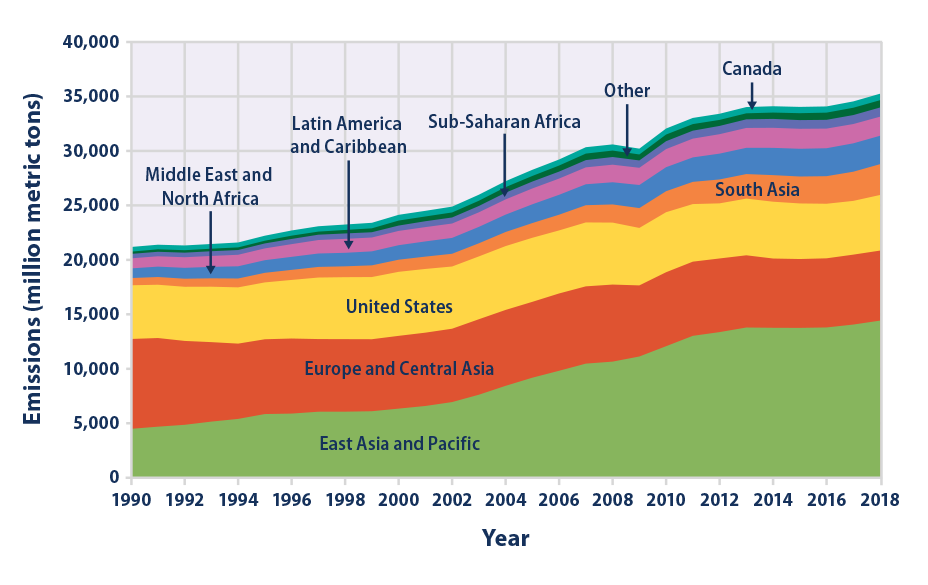
One chart that shows just how skewed global emissions are China, the US and the EU produce 14 times more than the bottom 100 countries Global warming is the ultimate international problem It doesn't matter where you live, climate change is the most serious threat the planet faces today When it comes to the sources of the greenhouse gasesNOAA's Annual Greenhouse Gas Index (AGGI) is a yearly report on the combined influence of longlived greenhouse gases (atmospheric gases that absorb and radiate heat) on Earth's surface temperature The index compares the combined warming influence of these gases each year to their influence in 1990, the year that countries who signed the U Carbon dioxide (CO 2) is an important heattrapping (greenhouse) gas, which is released through human activities such as deforestation and burning fossil fuels, as well as natural processes such as respiration and volcanic eruptionsThe first graph shows atmospheric CO 2 levels measured at Mauna Loa Observatory, Hawaii, in recent years, with average seasonal cycle



Youxclg0bikhtm



Www Canada Ca Content Dam Eccc Documents Pdf Cesindicators Global Ghg Emissions Global Ghg Emissions En Pdf
The Carbon Cycle Greenhouse Gases (CCGG) research area operates the Global Greenhouse Gas Reference Network, measuring the atmospheric distribution and trends of the three main longterm drivers of climate change, carbon dioxide (CO 2), methane (CH 4), and nitrous oxide (N 2 O), as well as carbon monoxide (CO) which is an important indicator of air pollution Background Increasing emissions of greenhouse gases due to human activities worldwide have led to a substantial increase in atmospheric concentrations of longlived and other greenhouse gases (see the Atmospheric Concentrations of Greenhouse Gases indicator) Every country around the world emits greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, meaning the root cause of climate change is truly globalThis chart summarizes the global sources of greenhouse gases If there's one key takeaway from this chart, it's this No single piece of the global economy accounts for the lion's share of greenhouse gas emissions In other words, there's no main culprit, no magic bullet




5 Charts Show How Your Household Drives Up Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions Pbs Newshour Weekend



Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions Data Greenhouse Gas Ghg Emissions Us Epa
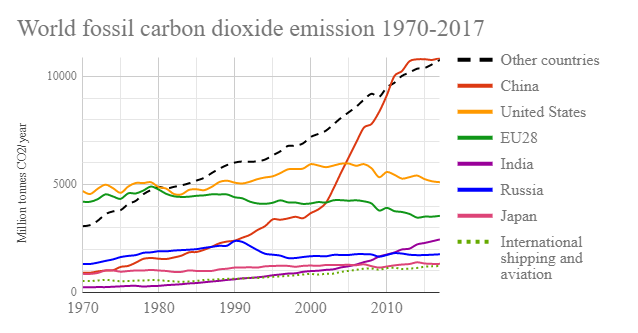
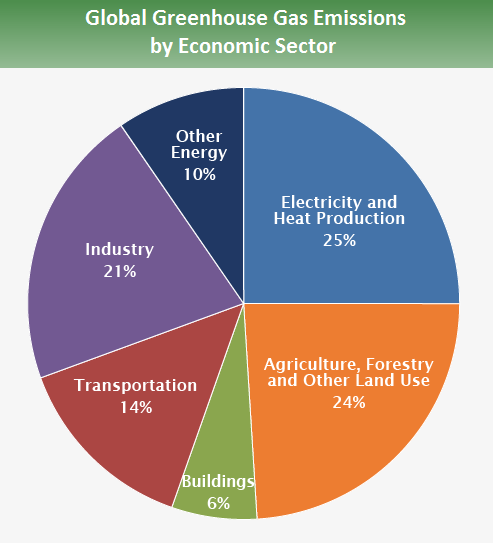
This chart shows the breakdown of total greenhouse gases (the sum of all greenhouse gases, measured in tonnes of carbon dioxide equivalents) by sector Here we see that electricity and heat production are the largest contributor to global emissions Cause of global warming Almost 100% of the observed temperature increase over the last 50 years has been due to the increase in the atmosphere of greenhouse gas concentrations like water vapour, carbon dioxide (CO 2), methane and ozoneGreenhouse gases are those gases that contribute to the greenhouse effect (see below) The distribution of global greenhouse gas emissions has reached an inflection point China's emissions exceeded developed nations combined in 19, a new Rhodium Group analysis concludes Why it matters "The shifting dynamics of global emissions — with China surpassing the developed world for the first time — means that meeting the Paris goals will




Greenhouse Gas Emissions By Country And Sector Infographic News European Parliament



File Greenhouse Gas By Sector 00 Svg Wikimedia Commons
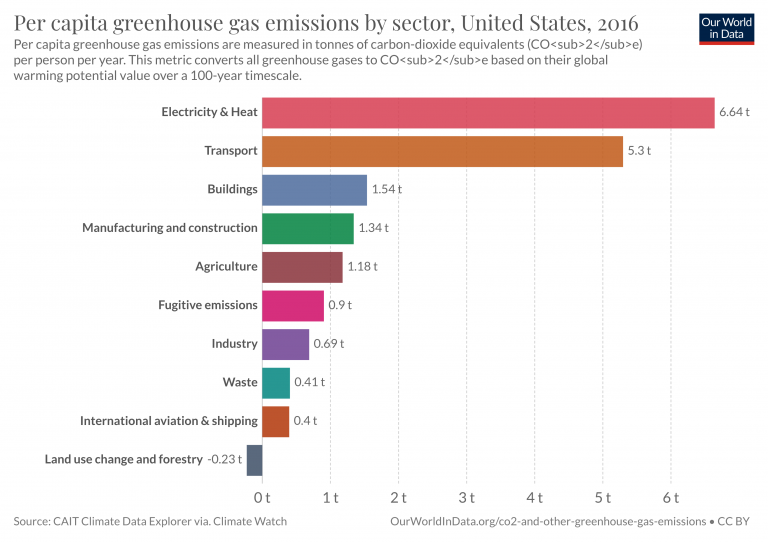
Greenhouse gases come from all sorts of everyday activities, such as using electricity, heating our homes, and driving around town The graph to the right shows which activities produce the most greenhouse gases in the United States These greenhouse gases don't just stay in one place after they're added to the atmosphereA greenhouse gas (GHG or GhG) is a gas that absorbs and emits radiant energy within the thermal infrared range, causing the greenhouse effect The primary greenhouse gases in Earth's atmosphere are water vapor (H 2 O), carbon dioxide (CO 2), methane (CH 4), nitrous oxide (N 2 O), and ozone (O 3)Without greenhouse gases, the average temperature of Earth's surface would These graphs depict the global average abundances of the major, wellmixed, longlived greenhouse gases carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, CFC12 and CFC11 from the NOAA global air sampling network plotted since the beginning of 1979



Greenhouse Gas Emissions Our World In Data



Near Real Time Monitoring Of Global Co 2 Emissions Reveals The Effects Of The Covid 19 Pandemic Nature Communications
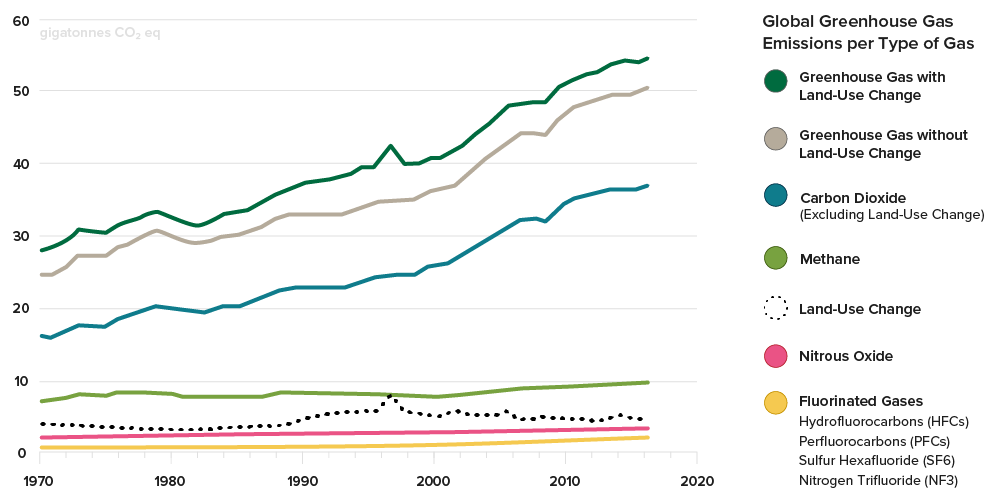
But CO 2 is not the only greenhouse gas Others, including methane and nitrous oxide, have also had a significant impact on global warming to date The first interactive chart shows per capita greenhouse gas emissions This is measured as the sum of all greenhouse gases, and given by a metric called 'carbon dioxide equivalents'This chart shows the change in global greenhouse gas emissions over time Greenhouse gases are measured in 'carbon dioxideequivalents' (CO 2 e) Today, we collectively emit around 50 billion tonnes of CO 2 e each year This is more than 40% higher than emissions in 1990, which were around 35 billion tonnes Energy consumption is by far the biggest source of humancaused global greenhouse gas emissionsat 73% of the total GHGs Industry is the fastestgrowing source of GHGs since 1990, with the
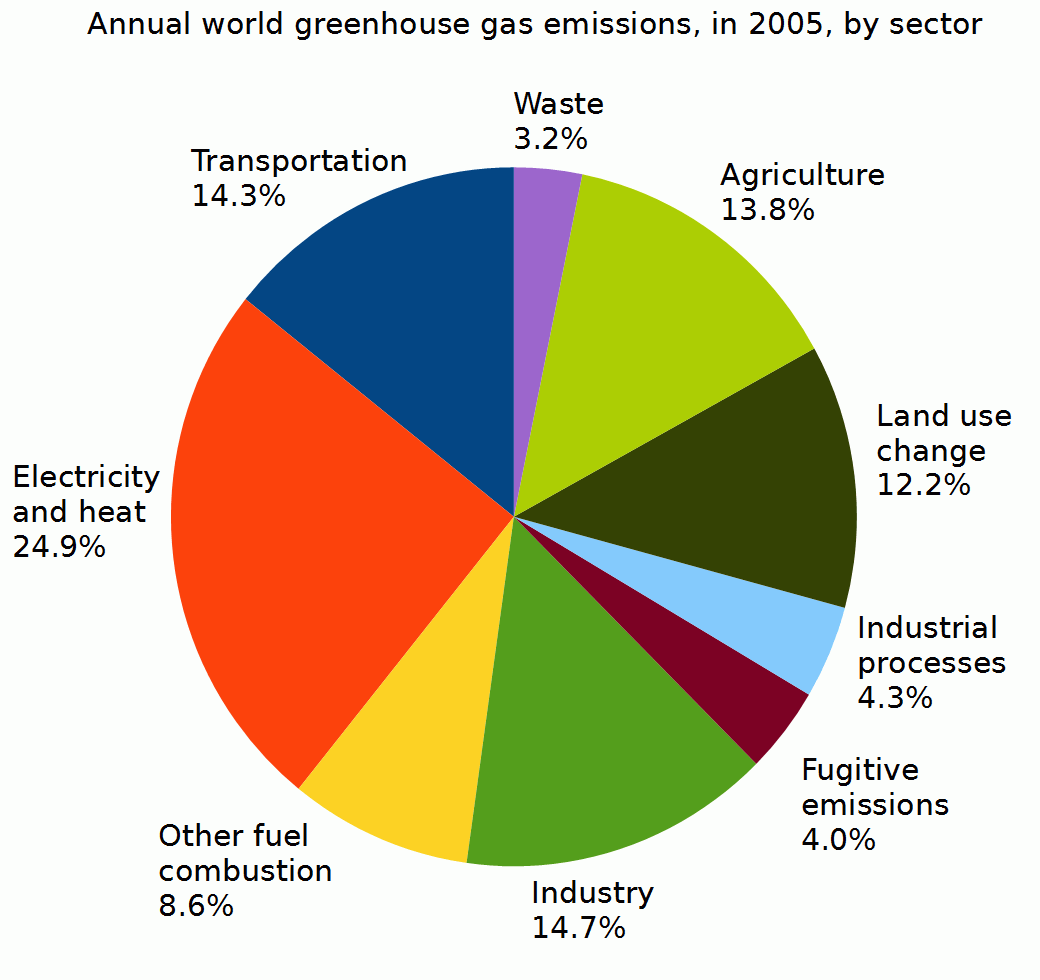



File Annual World Greenhouse Gas Emissions In 05 By Sector Png Wikimedia Commons



Chart China Leads Greenhouse Gas Emissions Worldwide Statista
In this post I present only one chart, but it is an important one – it shows the breakdown of global greenhouse gas emissions in 16 2 This is the latest breakdown of global emissions by sector, published by Climate Watch and the World Resources Institute 3, 4You are About to View Greenhouse Gas Quantities from Suppliers Important Information about this Data Set Suppliers are facilities or entities that supply certains products (eg, fossil fuels or industrial gases) into the economy that, when combusted, released, orThe greenhouse effect that has maintained the Earth's temperature at a level warm enough for human civilization to develop over the past several millennia is controlled by noncondensable gases, mainly carbon dioxide, CO 2, with smaller contributions from methane, CH 4, nitrous oxide, N 2 O, and ozone, O 3 Since the middle of the th
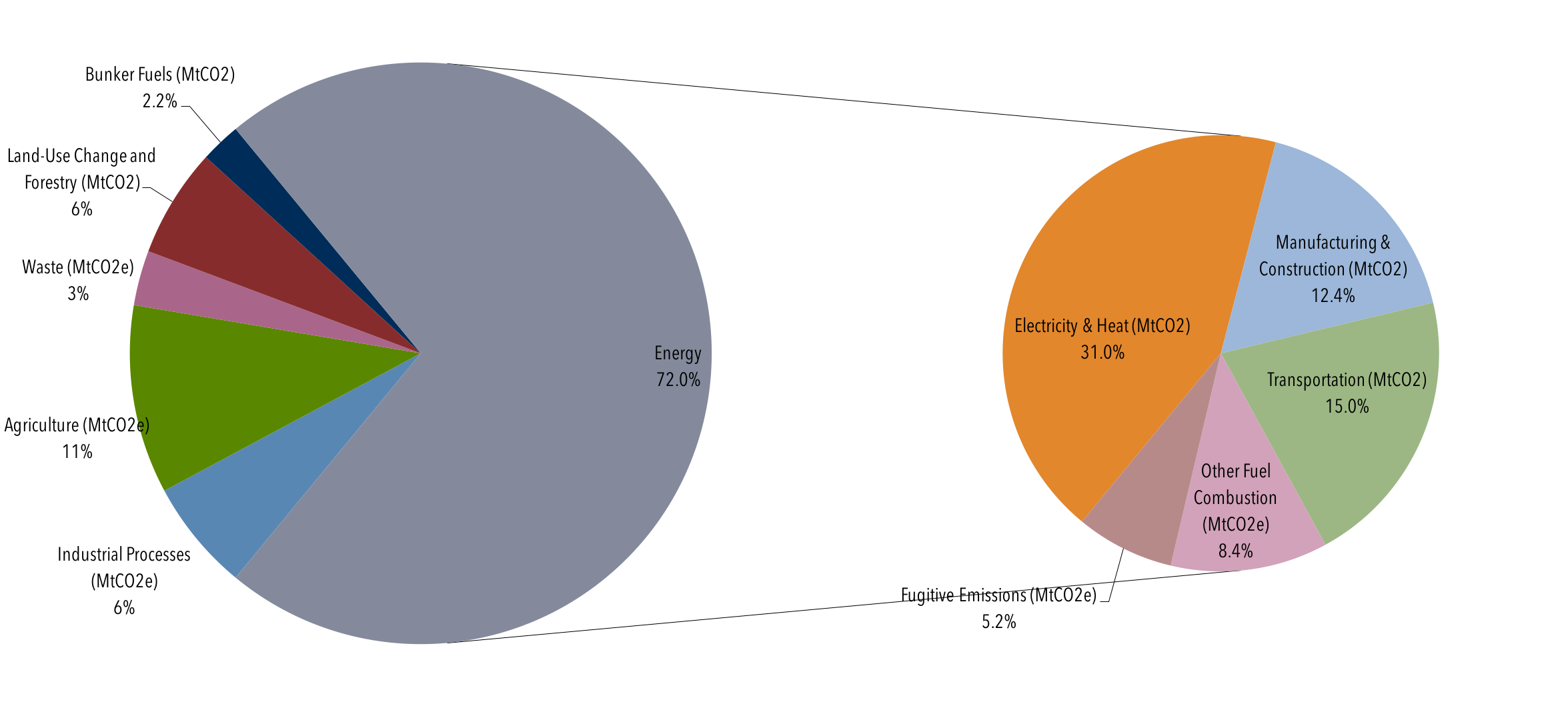



Global Emissions Center For Climate And Energy Solutions
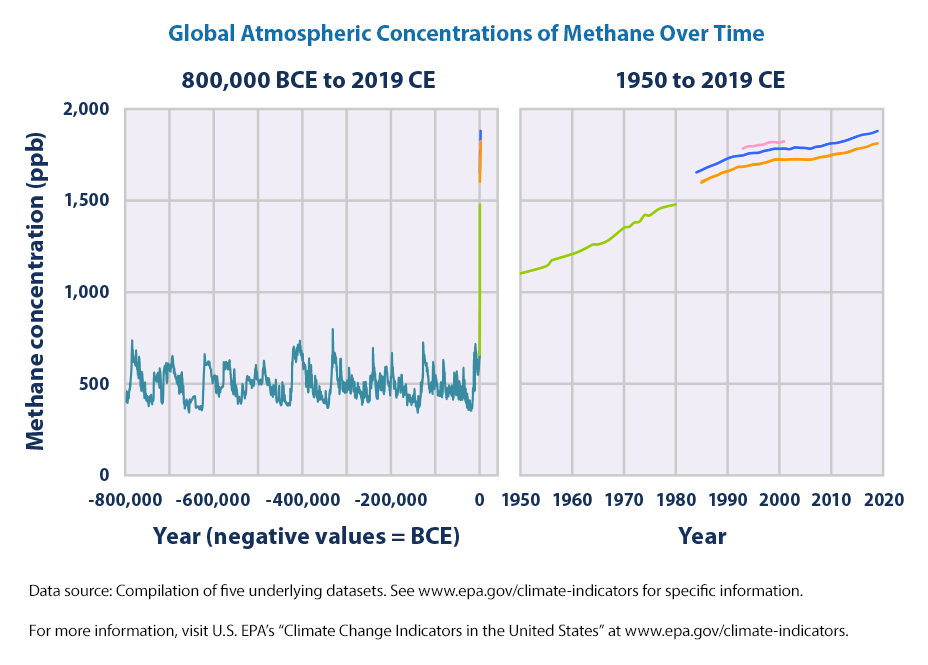



Youxclg0bikhtm
The graphs show monthly mean carbon dioxide globally averaged over marine surface sites The Global Monitoring Division of NOAA/Earth System Research Laboratory has measured carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases for several decades at a globally distributed network of air sampling sites Conway, 1994The last four complete years plus the current yearBased on global emissions from 04Greenhouse gases from human activities are the most significant driver of observed climate change since the mid th century 1 The indicators in this chapter characterize emissions of the major greenhouse gases resulting from human activities, the concentrations of these gases in the atmosphere, and how emissions and concentrations have changed over time




Pie Chart That Shows Country Share Of Greenhouse Gas Emission 30 Comes From China 15 From The Unite Greenhouse Gases Greenhouse Gas Emissions Ghg Emissions



Greenhouse Gas Emissions Our World In Data
The usual way of comparing greenhouse gases is through a single conversion factor, called the global warming potential, which uses a somewhat arbitrarily chosen time horizon of 100 years For methane, this is usually given as a factor of 25 (that is, methane is 25 times more potent than carbon dioxide) NASA's Global Climate Change website hosts an extensive collection of global warming resources for media, educators, weathercasters and public speakers Browse by topic and by media type, including videos, social media shareables, infographics, quizzes and interactives browse resourcesGlobal average abundances of the major, wellmixed, longlived greenhouse gases carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, CFC12 and CFC11 from the NOAA global air sampling network since the beginning of 1979 These five gases account for about 96% of the direct radiative forcing by longlived greenhouse gases since 1750




5 Charts Show How Your Household Drives Up Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions Pbs Newshour Weekend




Greenhouse Gas Emissions By Country And Sector Infographic News European Parliament
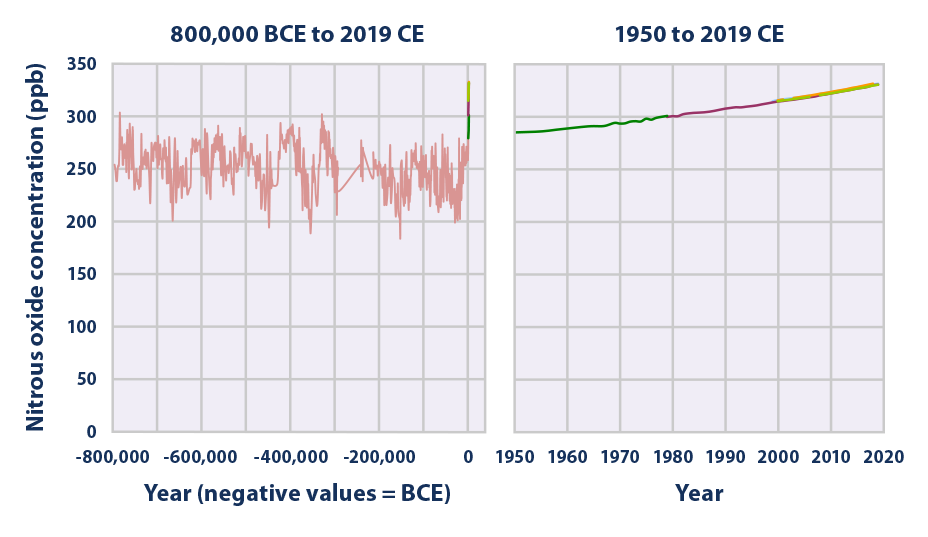
Global atmospheric concentrations of carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, and certain manufactured greenhouse gases have all risen significantly over the last few hundred years (see Figures 1, 2, 3, and 4)Top Ten Places That Emit Greenhouse Gases Created with Highcharts 901 Emissions in 17 (millions of metric tons of carbon dioxide equivalent) Chart title China United States India European Union (27) Russia Indonesia Brazil Japan Iran South Korea 0 2k 4k 6k 8k 10k 12k 14k World101 Council on Foreign Relations CFRorgThe gases present in the atmosphere for example ozone, methane, carbon dioxide, water vapour and chlorofluorocarbons are called greenhouse gases, they absorb some heat thereby restricting the heat to escape our atmosphere These gases add to the heating of the atmosphere and result in global warming In places where the temperature is low, we




Emissions Of The Powerful Greenhouse Gas Sf6 Are Rising Rapidly World Economic Forum
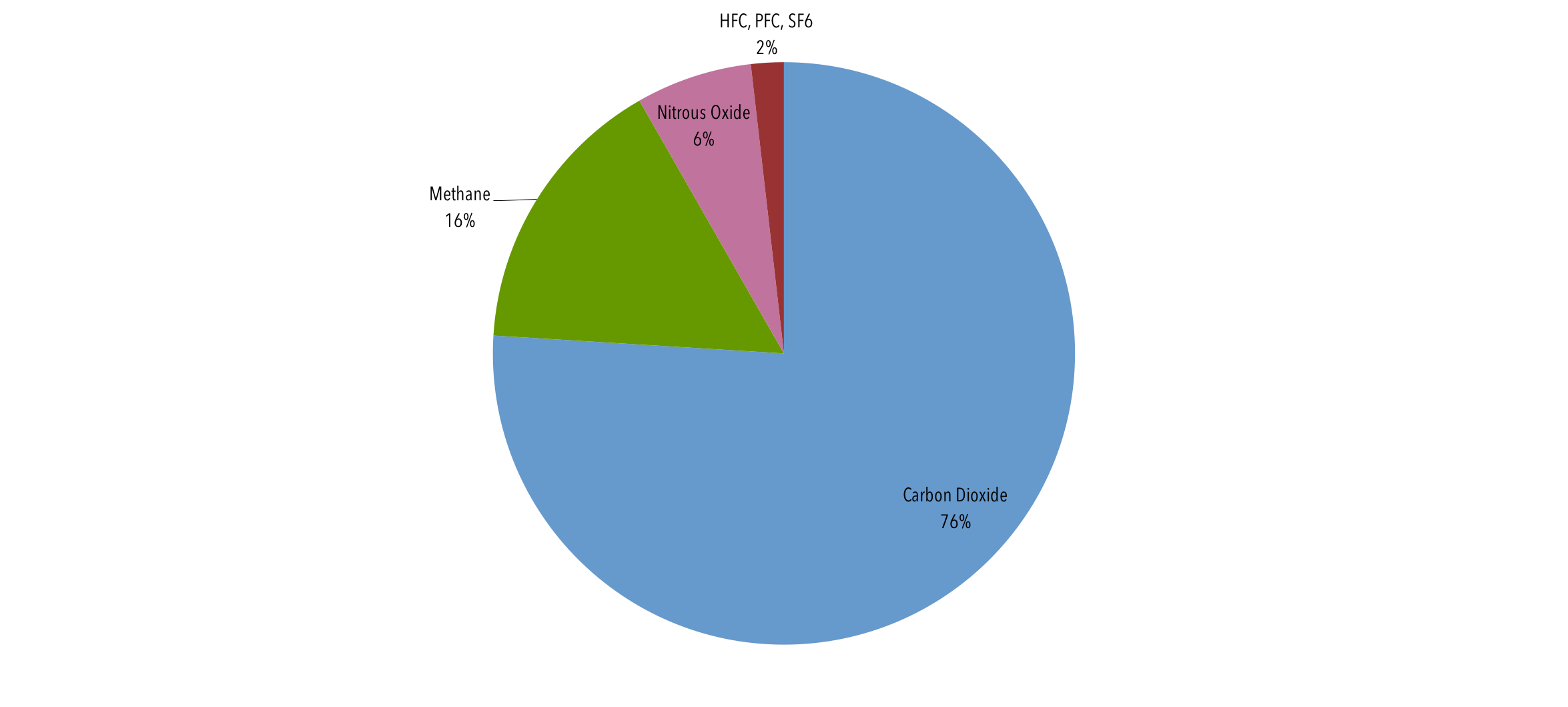



Global Emissions Center For Climate And Energy Solutions
That approach in effect makes carbon dioxide, CO 2, the prevailing "currency" of greenhouse gases and global warming Let's consider the principal GHGs one at a time, starting with water vapor, the most abundant greenhouse gas in the atmosphere according to NOAA's National Climatic Data Center (NCDC)Main Greenhouse Gases Multiple gases contribute to the greenhouse effect that sets Earth's temperature over geologic time Small changes in the atmospheric concentration of these gases can lead to changes in temperature that make the difference between ice ages when mastodons roamed the Earth, and the sweltering heat in which the dinosaurs livedIt took ~240 years for the AGGI to go from 0 to 1, ie, to reach 100%, and 30 years for it to increase by another 47% In terms of CO 2 equivalents, the atmosphere in contained 504 ppm, of which 412 is CO 2 alone The rest comes from other gases



Greenhouse Gas Emissions From The Energy Sector Geog 438w Human Dimensions Of Global Warming




Global Gas Emissions Climate Energy And Society College Of Liberal Arts Auburn University
During 17, NOAA's Global Greenhouse Gas Reference Network Measurements showed that concentrations of CO 2 in the atmosphere rose by 23 parts per million, following record increases of 29 ppm in 16 and 15 This is the sixth consecutive year CO 2 rose by 2 ppm or more Prior to 12, backtoback annual increases of 2 ppm or greater Electricity and Heat Production (25% of 10 global greenhouse gas emissions) The burning of coal, natural gas, and oil for electricity and heat is the largest single source of global greenhouse gas emissions;The planet's average surface temperature has risen about 212 degrees Fahrenheit (118 degrees Celsius) since the late 19th century, a change driven largely by increased carbon dioxide emissions into the atmosphere and other human activities 4 Most of the warming occurred in the past 40 years, with the seven most recent years being the warmest The years 16 and are tied for



Greenhouse Gas Emissions Our World In Data
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/16185122/gw_graphic_pie_chart_co2_emissions_by_country_2015.png)



Climate Change Animation Shows Us Leading The World In Carbon Emissions Vox
Greenhouse Gas Emissions Data The Oregon Global Warming Commission submits a report to the Oregon Legislature every two years, publishing data on current greenhouse gas emissions, trends, and steps we need to take to reduce emissions The data below is taken from the 18 Oregon Global Warming Commission report The majority of greenhouse gas emissions from US household transportation are created domestically, as measured in megatons of carbon dioxide equivalent Chart by The Conversation, CCBYNDGreenhouse Gases such as carbon dioxide is the primary cause for the Greenhouse Effect The major contributors to the greenhouses gases are factories, automobiles, deforestation , etc The increased number of factories and automobiles increases the amount of these gases



Greenhouse Gas Emissions Our World In Data




Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions By Sector Download Scientific Diagram
In its Global Energy Review, published on Tuesday, the IEA found that global carbon emissions from energy use, which accounts for the great majority of greenhouse gas emissions, were on course to Greenhouse gases emissions in the EU and in the world The charts above list EU countries by total greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions in 17 and the infographic below shows the world's top greenhouse gas emitters in 15 The EU is the third biggest emitter behind China and the United State and followed by India and Russia China is the biggest emitter at 26% of global greenhouse gas emissions, followed by the United States at 13%, the European Union at 78% and India at 67% Most of the top 10 emitters have higher emissions per person than the world average (around 68 tCO2e per person) Among the top 10 total greenhouse gas emitters, Canada and the United




These Are The Causes Of Greenhouse Gases Greenhouse Gases List Of Positive Words Greenhouse Gas Emissions




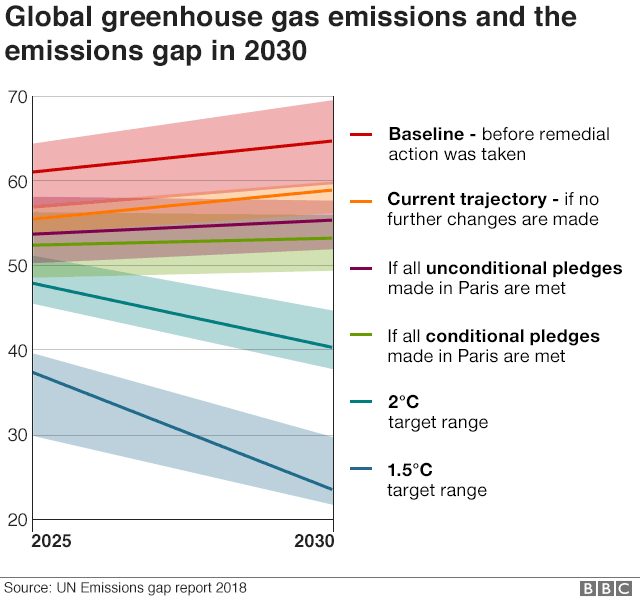
Major Greenhouse Gas Reductions Needed By 50 Ipcc Climate Central



Co And Greenhouse Gas Emissions Our World In Data




Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions In The Unmitigated Reference Download Scientific Diagram



1



1




Dnr Reports 3 Increase In Iowa Greenhouse Gas Emissions Iowa Environmental Focus
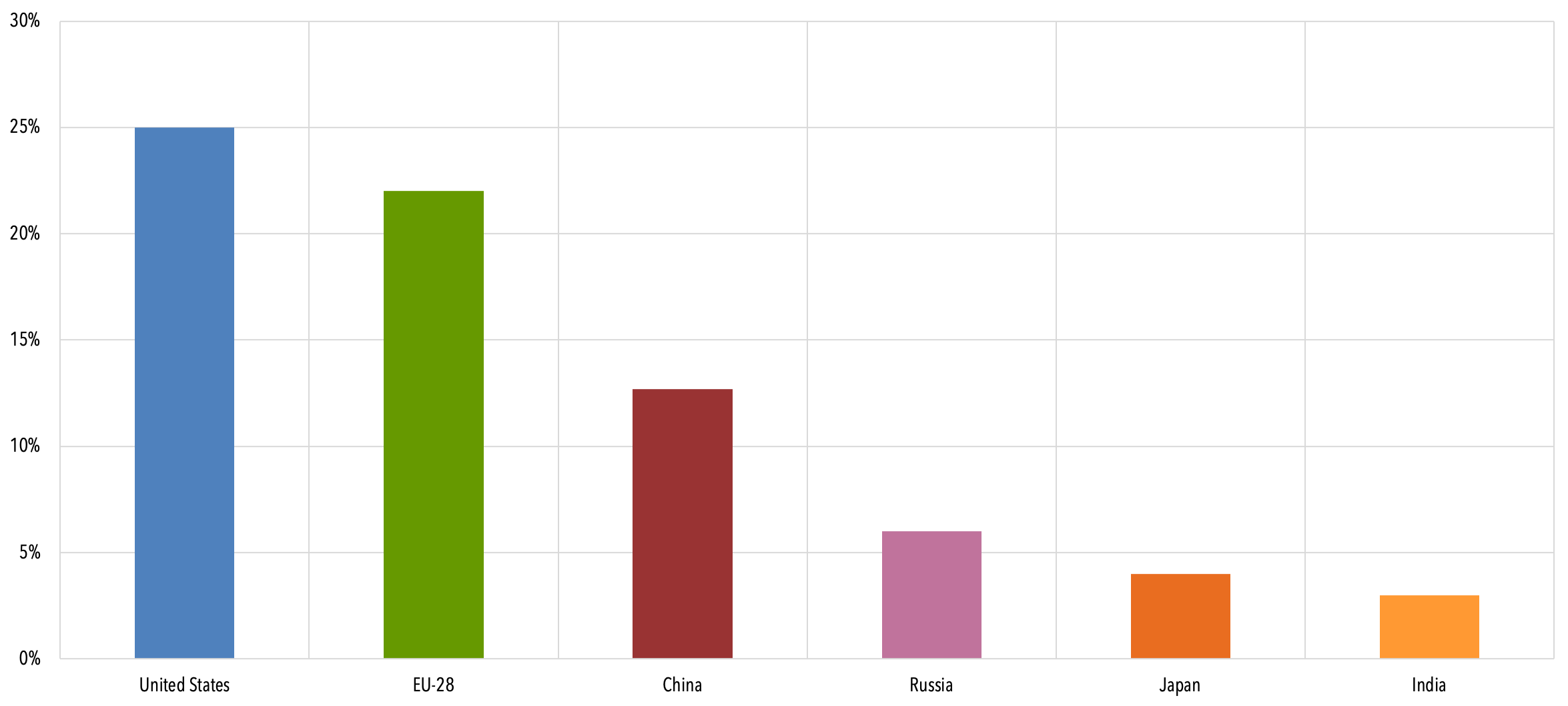



Global Emissions Center For Climate And Energy Solutions



Chart Europe S Biggest Greenhouse Gas Emitters Statista




Greenhouse Gas Emissions By Country And Sector Infographic News European Parliament



Greenhouse Gas Emissions Our World In Data




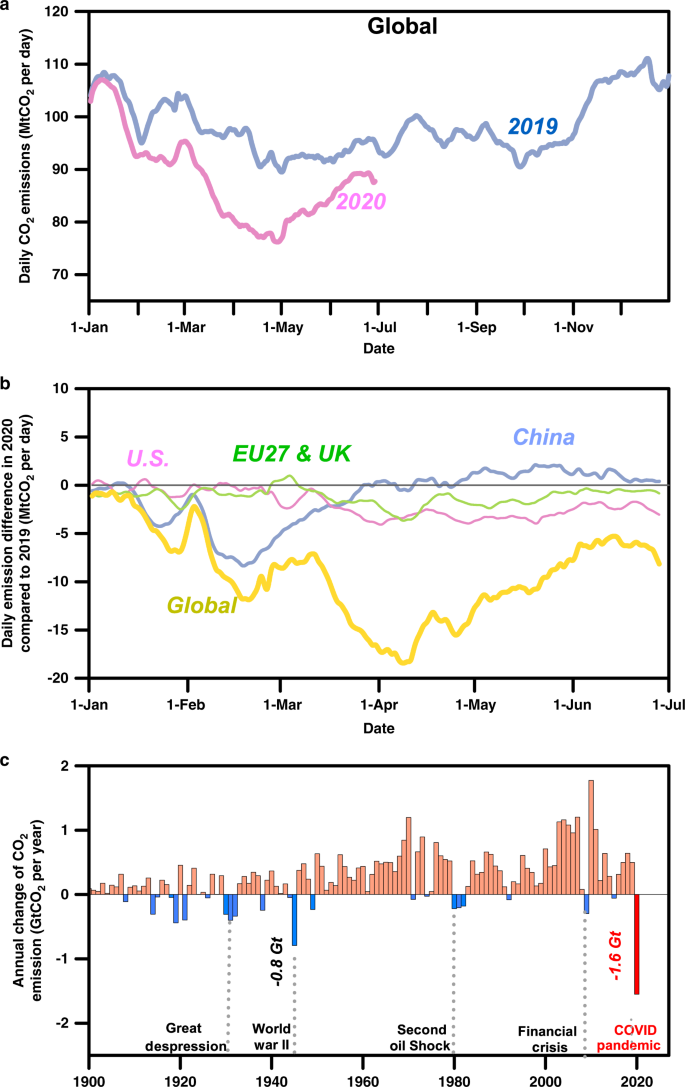
Greenhouse Gas Emissions Plunged 17 Percent During Pandemic The Washington Post




Greenhouse Effect 101 Nrdc



Global Emissions Center For Climate And Energy Solutions




This Graph Shows How The Total Amount Of Greenhouse Gas Emissions Has Been Increasing Around The World Greenhouse Gases Climate Change Greenhouse Gas Emissions




Where Do Greenhouse Gas Emissions Come From University Of California



Emissions By Sector Our World In Data
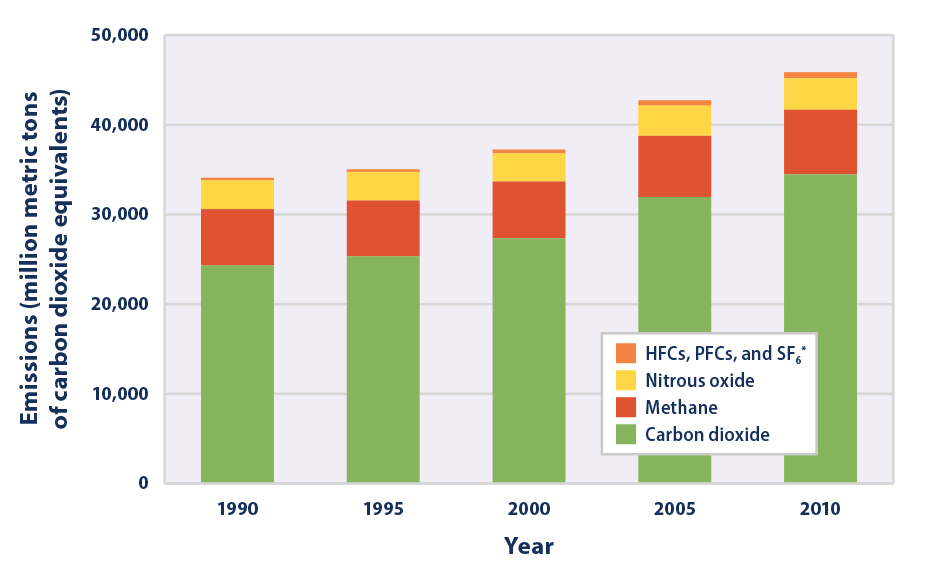



Climate Change Indicators Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions Climate Change Indicators In The United States Us Epa



Annual Ghg Index Aggi
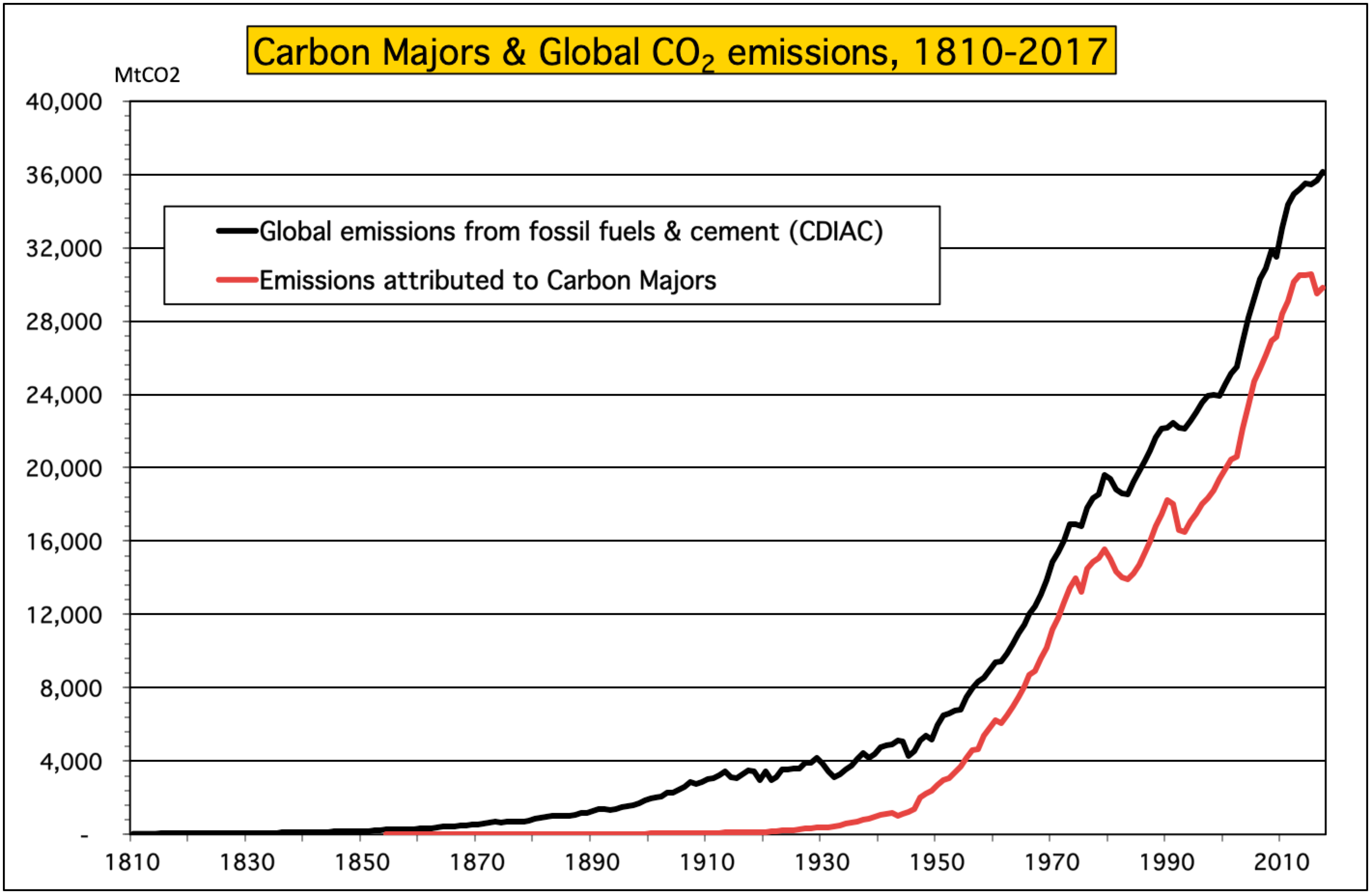



Climate Accountability Institute
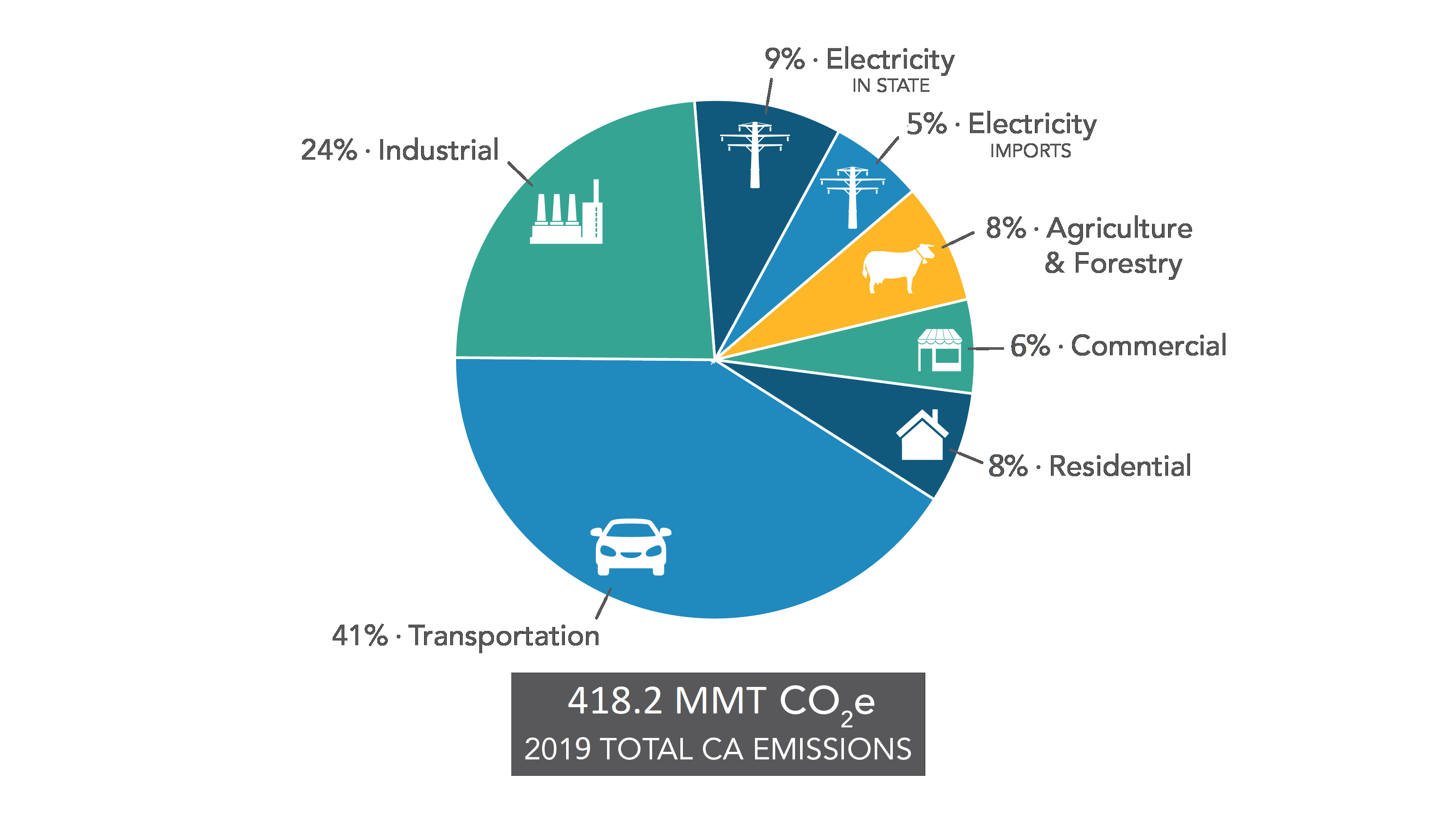



Ghg Emission Inventory Graphs California Air Resources Board




Greenhouse Gases A Student S Guide To Global Climate Change Us Epa Greenhouse Gases Climate Change Climate Change Activities
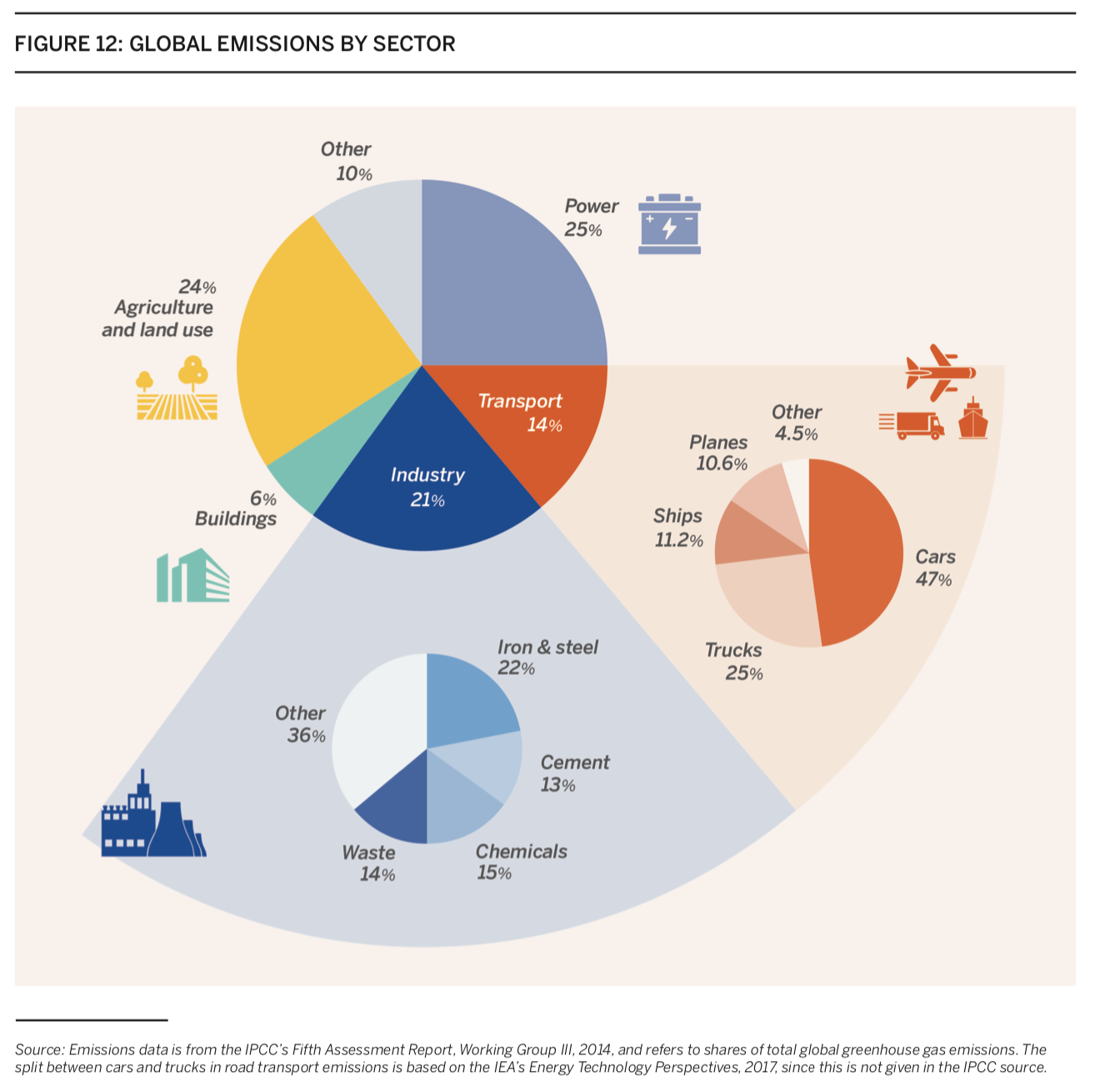



Charts Of The Week Tackling Climate Change




5 Charts Show How Your Household Drives Up Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions Greenhouse Gas Emissions Greenhouse Gases Carbon Footprint



Emissions By Sector Our World In Data




Greenhouse Gases Copernicus



Climate Basics For Kids Center For Climate And Energy Solutions




Noaa S Greenhouse Gas Index Up 41 Percent Since 1990 Welcome To Noaa Research




Greenhouse Gas Emissions Are Set To Rise Fast In 21 The Economist




Upload Wikimedia Org Wikipedia Commons E Ed Glo



Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions Data Greenhouse Gas Ghg Emissions Us Epa



1
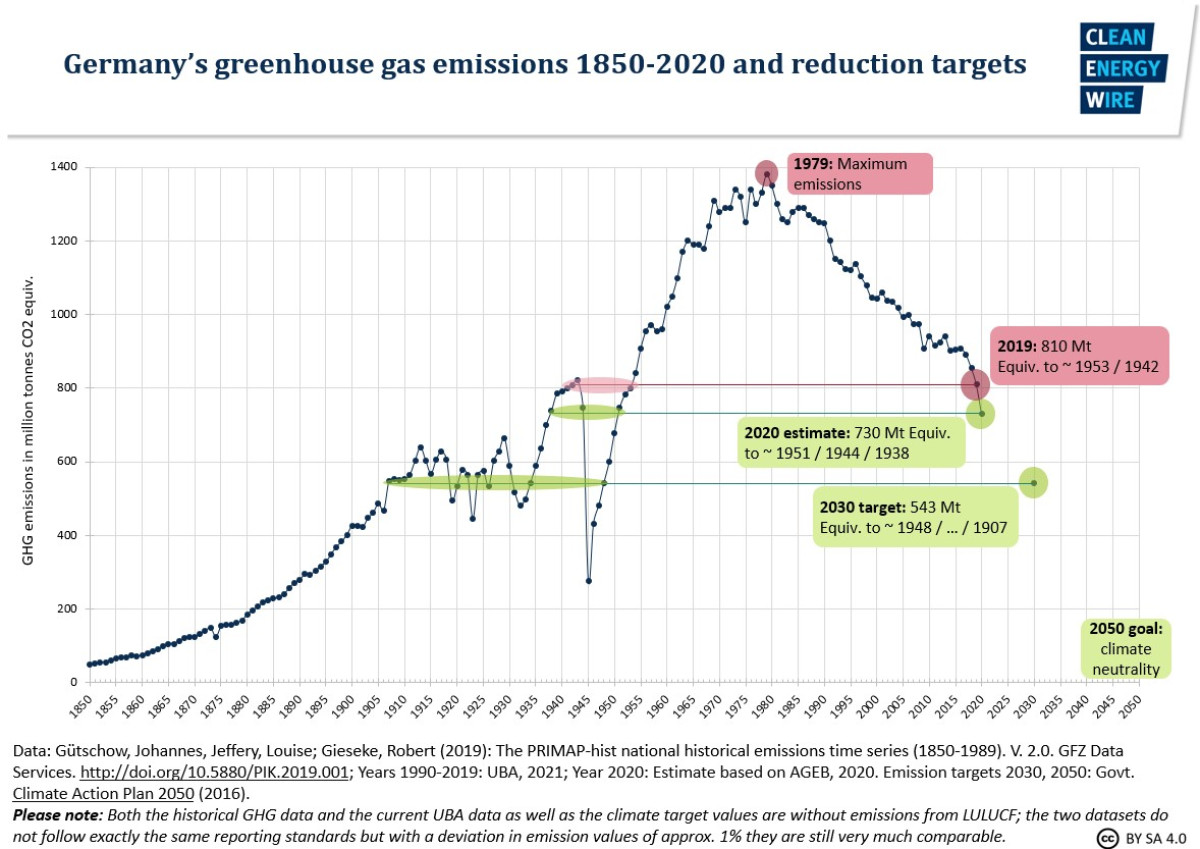



Germany S Greenhouse Gas Emissions And Energy Transition Targets Clean Energy Wire
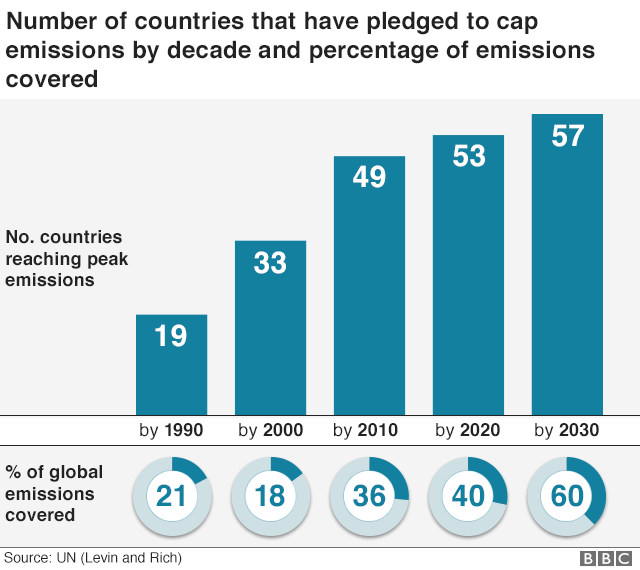



Climate Change Co2 Emissions Rising For First Time In Four Years c News



Emissions By Sector Our World In Data



Earthcharts Greenhouse Gas Emissions By Sector



Greenhouse Gas Emissions Wikipedia



What Are Greenhouse Gases What S Your Impact



Co And Greenhouse Gas Emissions Our World In Data



W Edyfjigr0fxm




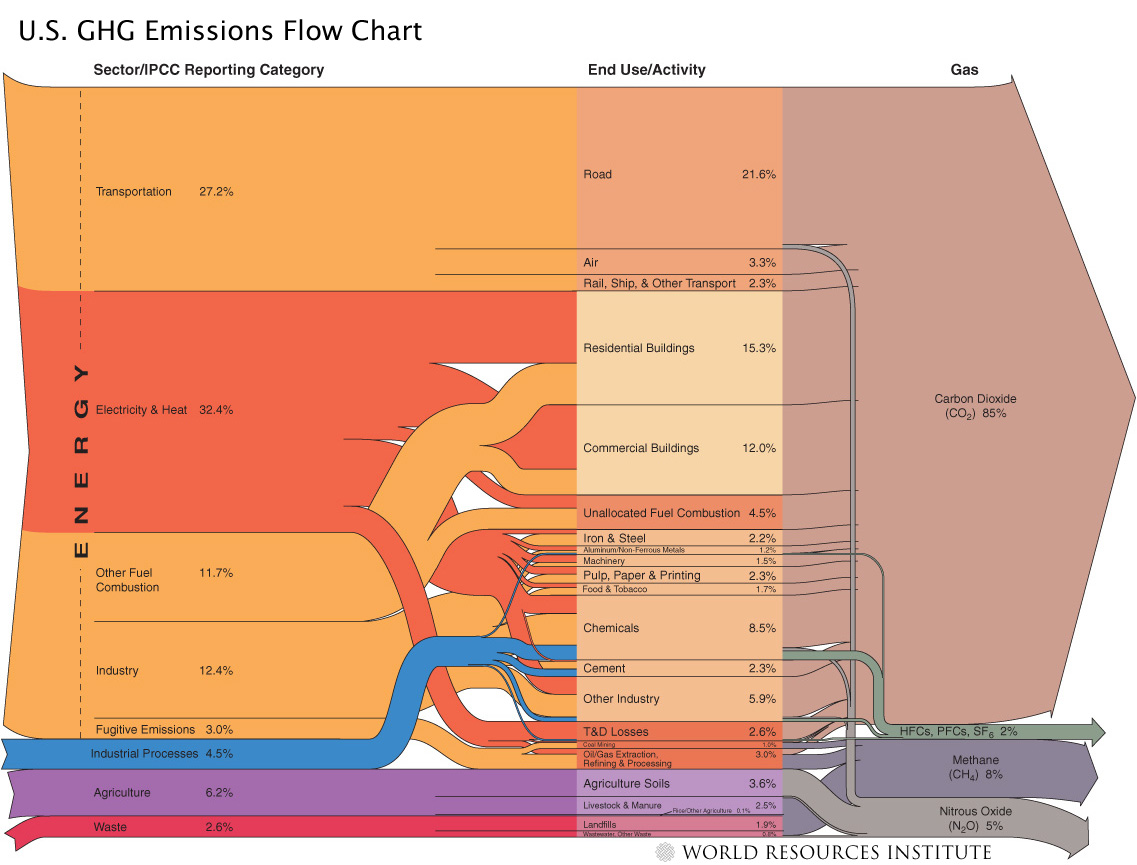
World Ghg Emissions Flow Chart Download Scientific Diagram



Chart Global Carbon Emissions Fall In Statista




Global Emissions Center For Climate And Energy Solutions
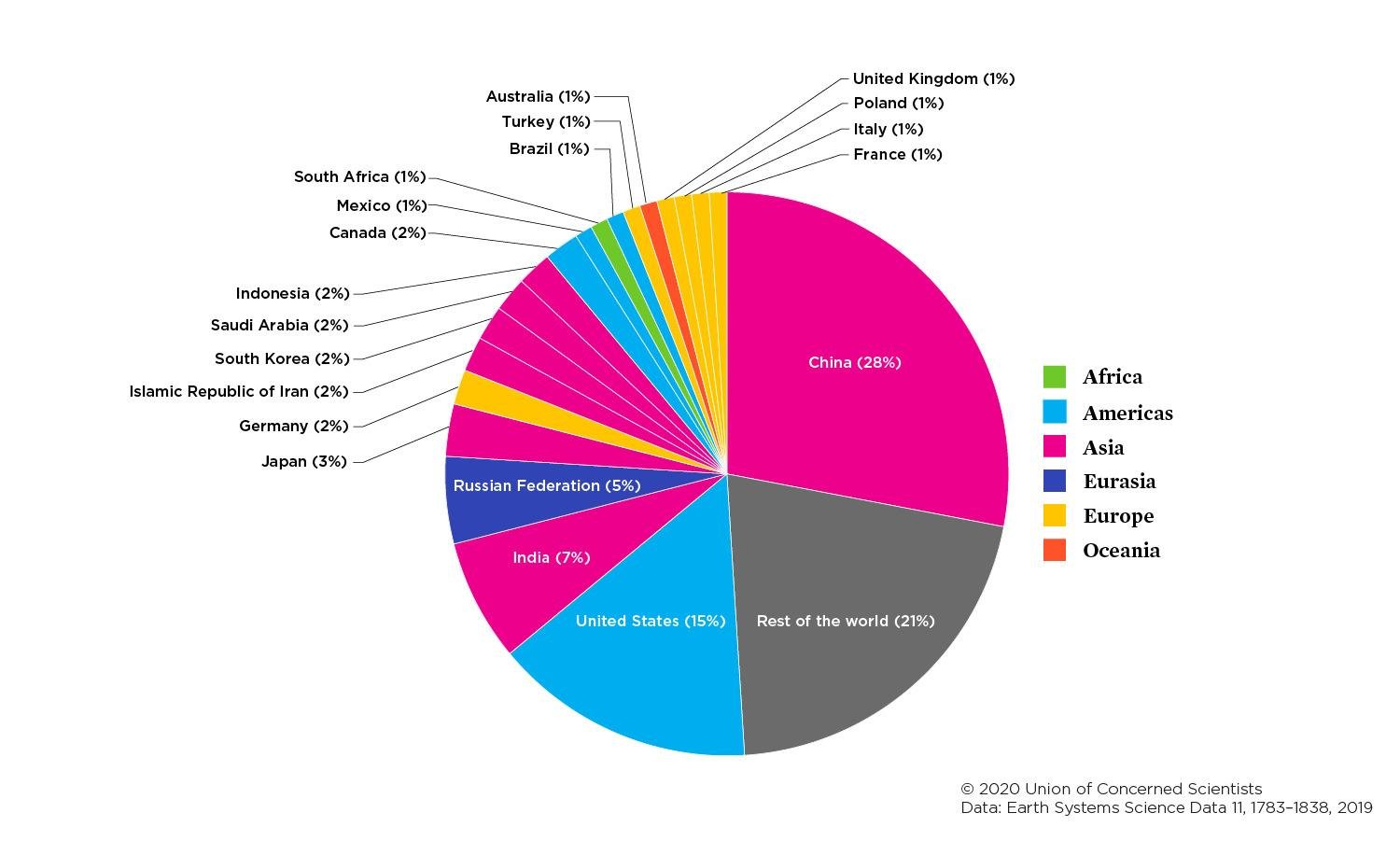



Each Country S Share Of Co2 Emissions Union Of Concerned Scientists



How To Stop Global Warming In 7 Steps Vox



Greenhouse Gas Emissions Our World In Data




Usgcrp Indicator Details Globalchange Gov



How Much Does Animal Agriculture And Eating Meat Contribute To Global Warming




Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions Data Us Epa
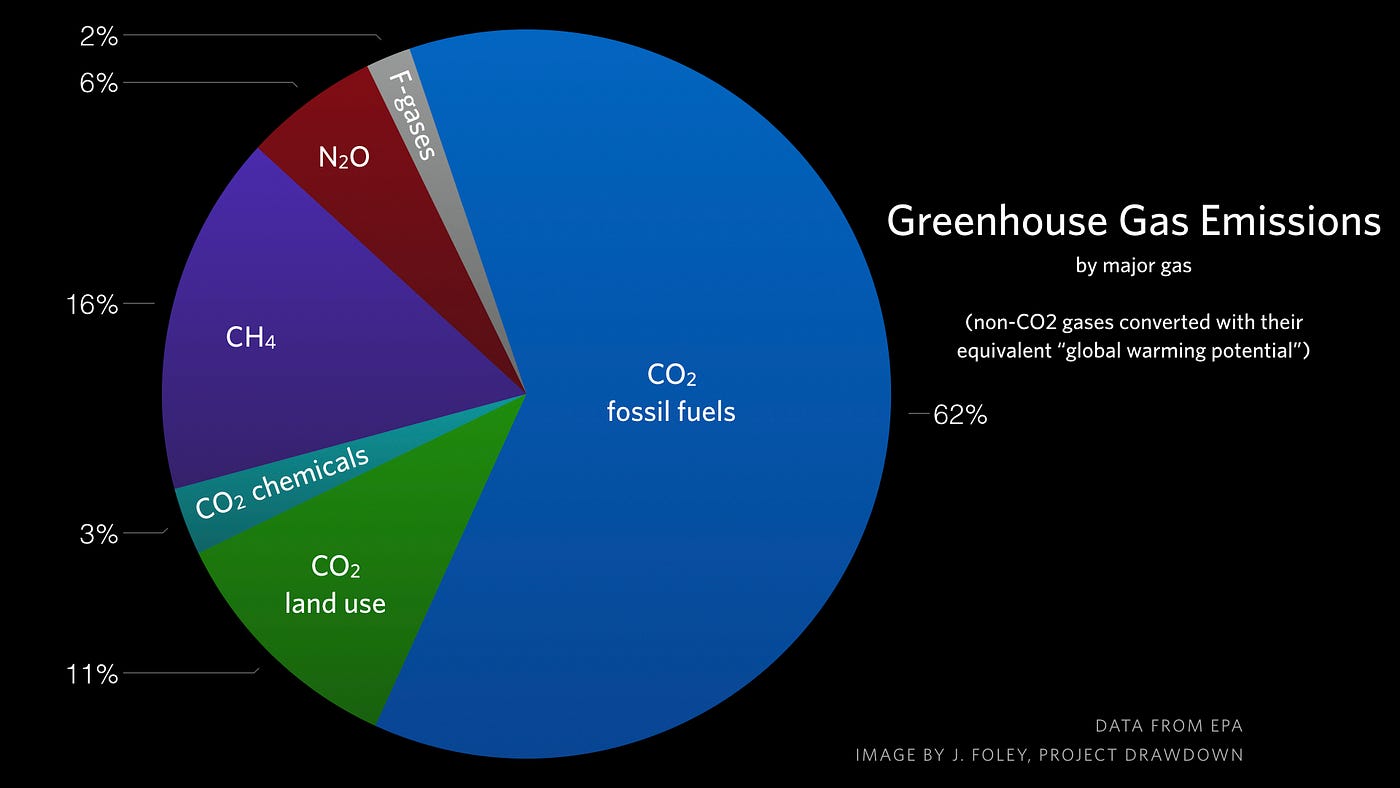



Major Causes Of Climate Change Globalecoguy Org




Chart The Hardest Emissions To Eliminate Solar Energy Infographic Greenhouse Gases Solar Energy Projects



Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions Plotted In Bar Mekko Sample Charts




Climate Change Annual Greenhouse Gas Index Noaa Climate Gov
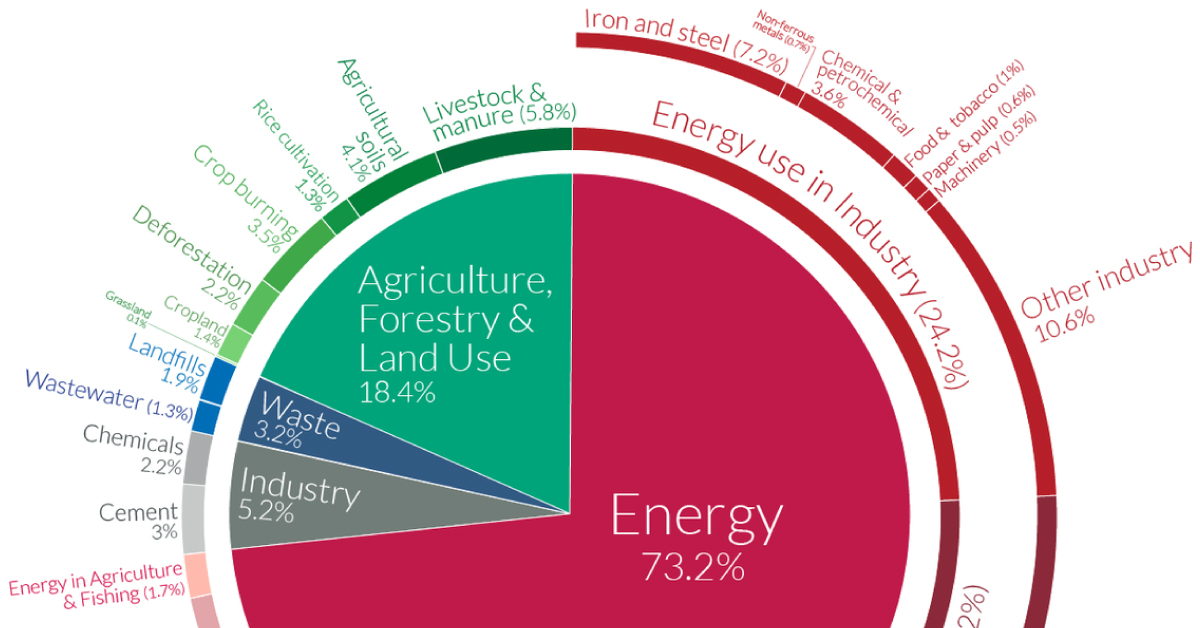



A Global Breakdown Of Greenhouse Gas Emissions By Sector




Greenhouse Gases A Student S Guide To Global Climate Change Us Epa
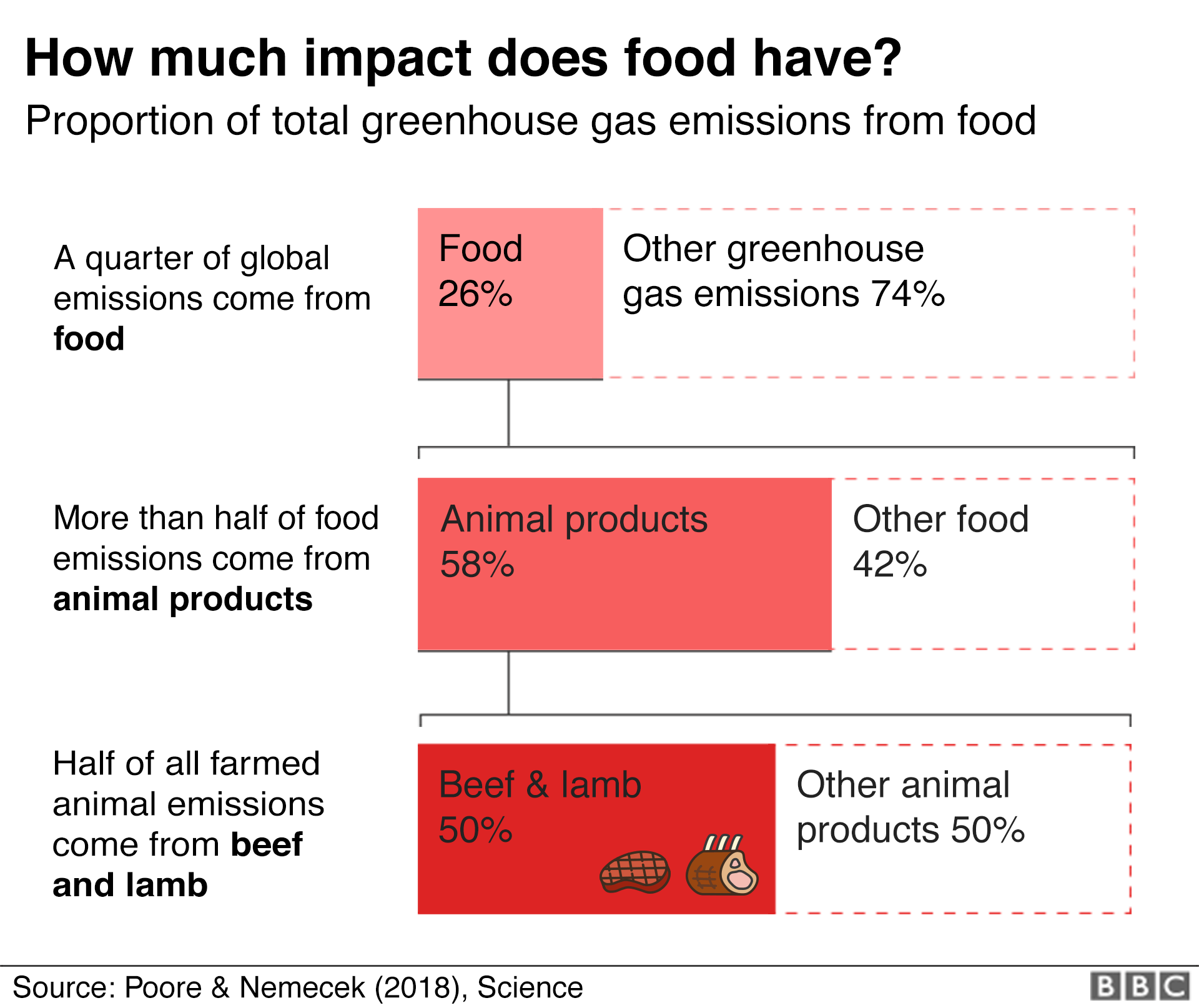



Climate Change Food Calculator What S Your Diet S Carbon Footprint c News




What Are Greenhouse Gases And Greenhouse Effect
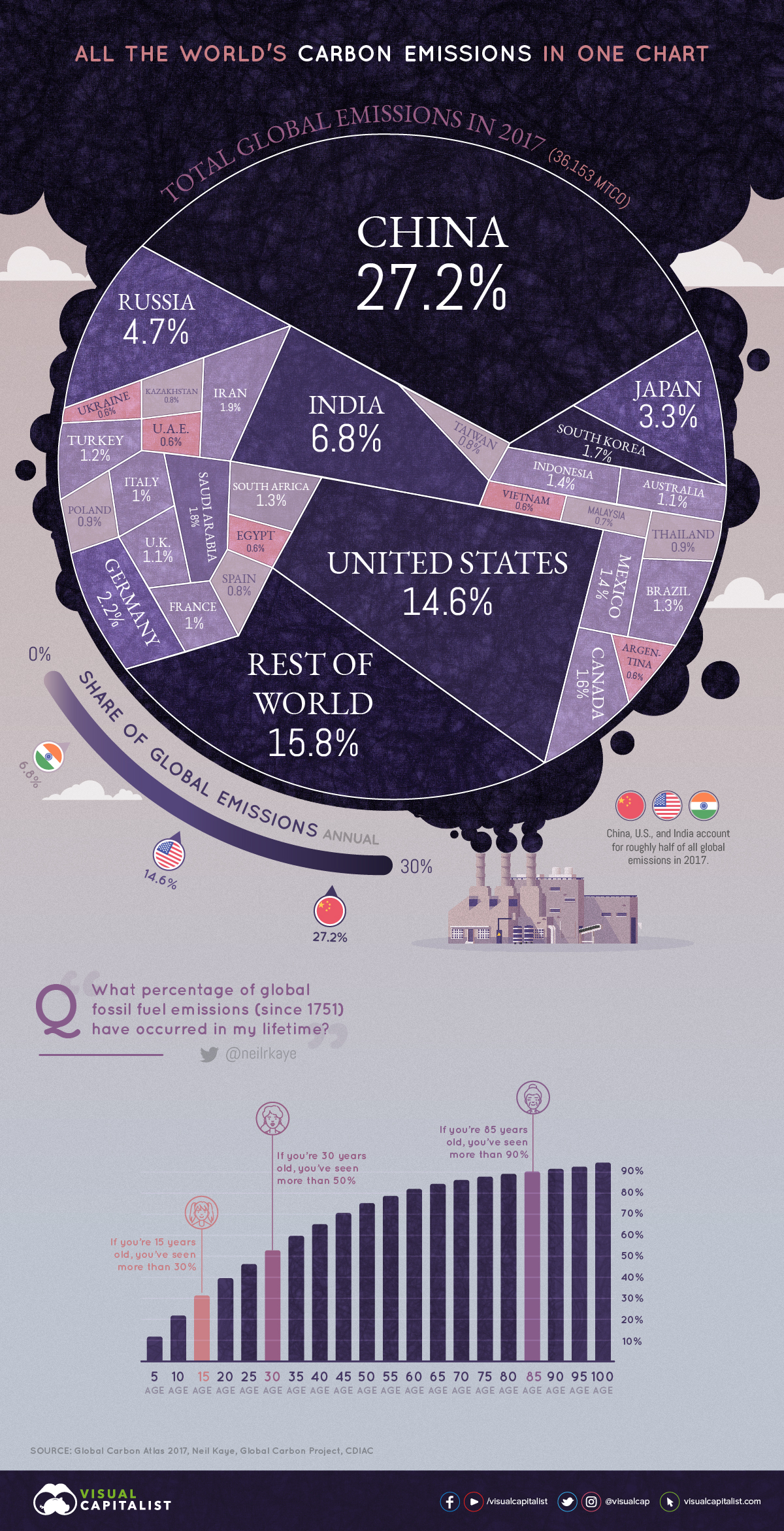



All Of The World S Carbon Emissions In One Giant Chart




4 Ways To Cut Plastic S Growing Greenhouse Gas Emissions Inside Climate News



Greenhouse Gas Global Greenhouse Warming



Climate Change Co2 Emissions Rising For First Time In Four Years c News



Breakdown Of Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions Attributable To Cattle Download Scientific Diagram




Greenhouse Gas Emissions Our World In Data




Emissions By Sector Our World In Data




I Pinimg Com Originals C5 78 65 Cf853d4eca




Greenhouse Gases A Student S Guide To Global Climate Change Us Epa
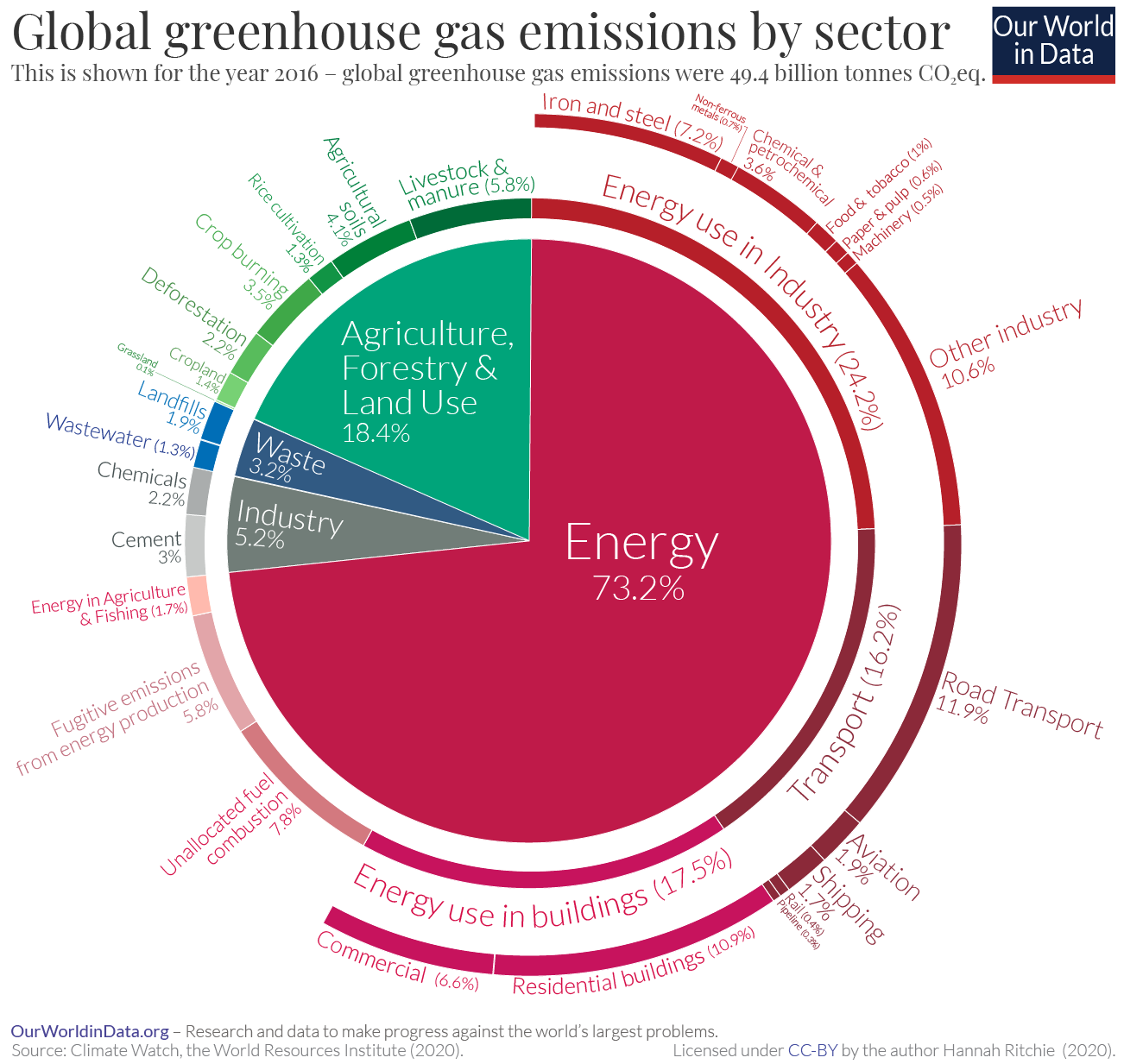



Sector By Sector Where Do Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions Come From Our World In Data



Emissions By Sector Our World In Data




Greenhouse Gases A Student S Guide To Global Climate Change Us Epa



Co And Greenhouse Gas Emissions Our World In Data




Predicted Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions By Sres Scenario Download Scientific Diagram




Greenhouse Gas Emissions On A Global Level And Seven Large Countries Download Scientific Diagram



Cait Climate Data Explorer



Q Tbn And9gcqmwzplha10o63rh Nrmk3kjfwx0rrlr8vlri O2mhfgiawzf3g Usqp Cau
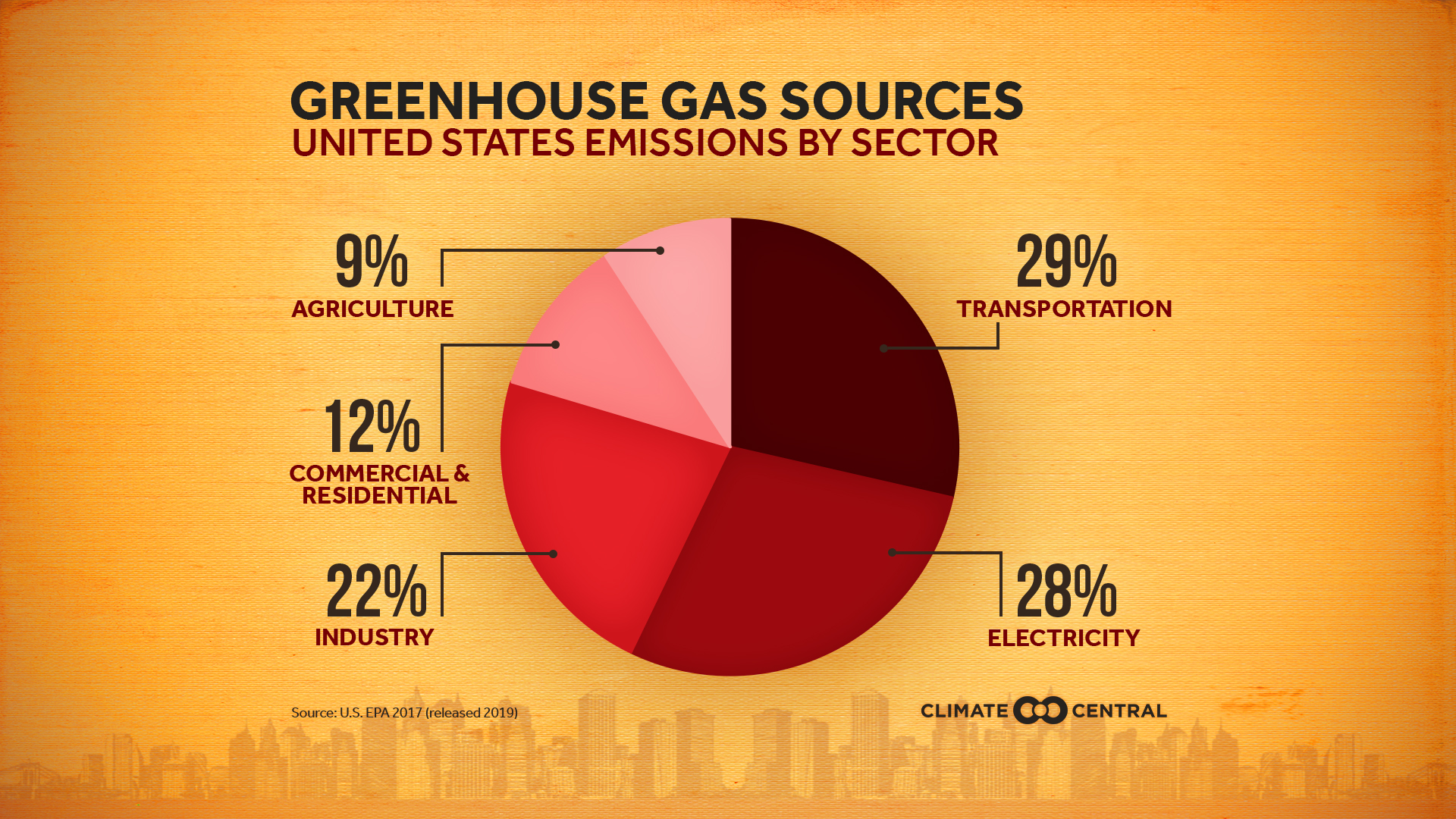



Emissions Sources Climate Central
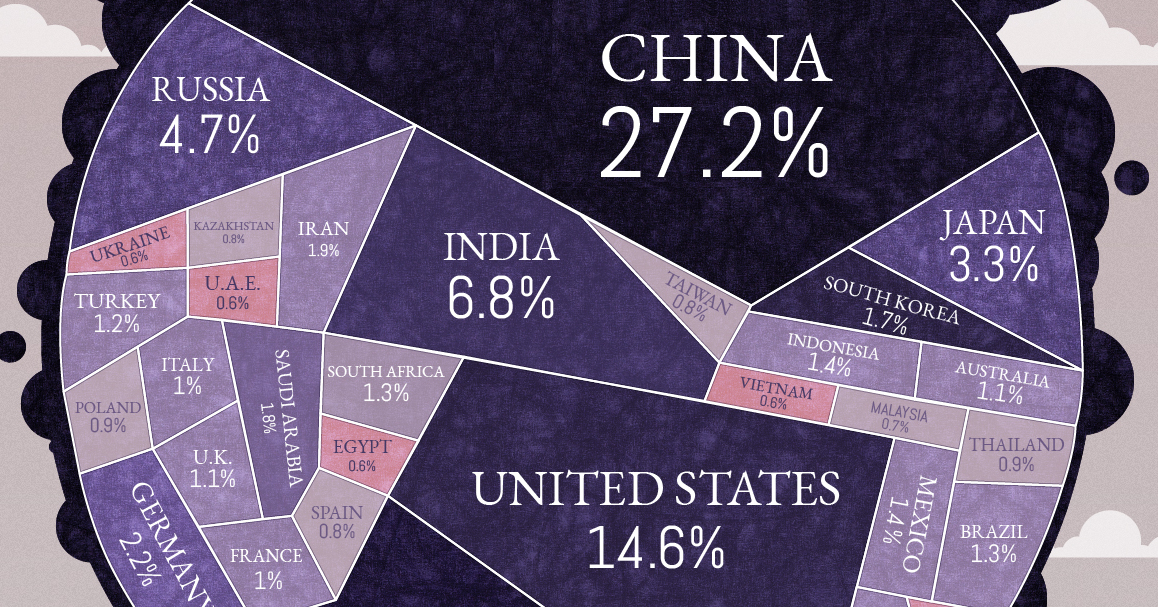



All Of The World S Carbon Emissions In One Giant Chart




Global Emissions Center For Climate And Energy Solutions




Greenhouse Gas Concentrations Surge To New Record World Meteorological Organization



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿